Package Exports
- @florentine-ai/api
Readme
Florentine.ai API - Talk to your MongoDB data
The Florentine.ai API lets you integrate natural language querying for your MongoDB data directly into your project.
Questions are transformed into MongoDB aggregations that can also directly be executed and answered in natural language.
Also has a couple of extra features under the hood, e.g.:
- Secure data separation for multi-tenant usage
- Semantic vector search/RAG support with automated embedding creation
- Advanced lookup support
- Exclusion of keys
[!NOTE] If you are looking for our MCP Server you can find it here.
Contents
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- Authentication
- Connect your LLM account
- First Request
- Return Types
- Secure Data Separation for multi-tenant usage
- Sessions
- Errors
Prerequisites
- Node.js >= v18.0.0
- A Florentine.ai account (create a free account here)
- A connected database and at least one analyzed and activated collection in your Florentine.ai account
- A Florentine.ai API Key (you can find yours on your account dashboard)
Installation
A detailed documentation of the API can be found here in our docs.
npm install @florentine-ai/apiAuthentication
import { Florentine } from '@florentine-ai/api';
const FlorentineAI = new Florentine({
florentineToken: '<FLORENTINE_API_KEY>'
});Connect your LLM account
Florentine.ai works as a bring your own key model, so you need to provide your LLM API key (OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Deepseek) in your API requests.
You have two options how you can add your LLM API key:
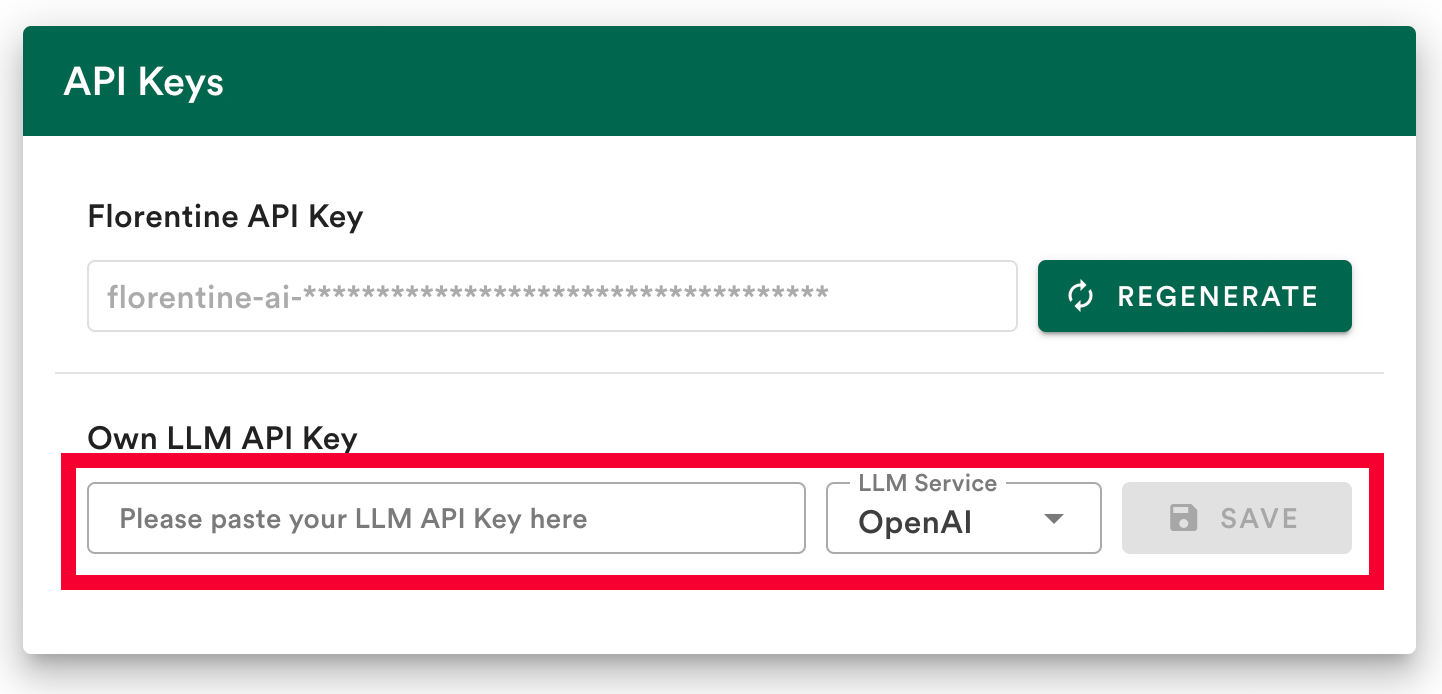
Option 1: Save your LLM key in your account (recommended)
The easiest way to connect to your LLM provider is to save your LLM API key in your Florentine.ai dashboard.
- Add your API key
- Select your LLM provider (OpenAI, Deepseek, Google or Anthropic)
- Click Save
Option 2: Provide your LLM key in API requests
If you prefer not to store the key in your Florentine.ai account or want to use multiple LLM keys, you can pass the key in your API request.
Add the values as llmService and llmKey to the class constructor object:
const FlorentineAI = new Florentine({
florentineToken: '<FLORENTINE_API_KEY>',
llmService: '<YOUR_LLM_SERVICE>', // one of: "openai", "google", "anthropic", "deepseek"
llmKey: '<YOUR_LLM_API_KEY>'
});[!NOTE] If you provide an
llmKeyinside the request, it will override any key stored in your account.
First Request
You should now be ready to send your first API request!
Come up with a question that can be answered via the data in your activated collection(s) and pass it to the .ask() method:
const FlorentineAI = new Florentine({
florentineToken: '<FLORENTINE_API_KEY>'
});
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: '<YOUR_QUESTION>',
sessionId: 'FIRST_REQUEST'
});By default, the API returns a natural language answer based on the aggregation results.
Imagine a tabletennis collection that records the results of the matches of two players.
If I ask the question Who won the last match? the answer might look similar to this:
{
"answer": "Frank won the last match. According to our records, he emerged as the winner, highlighting his strong performance in that game."
}Return Types
By default, the API returns a natural language answer to the question provided. However, what's happening in the background is actually three steps:
- Aggregation Generation: The question is converted into a MongoDB aggregation query.
- Query Execution: The aggregation runs against the database using the connection string you provided.
- Answer Generation: The structured result is transformed into a natural language answer.
You can choose which of these steps you want returned by specifying a returnTypes array with any combination of:
returnTypes Value |
Description | Expected Keys in Response |
|---|---|---|
"aggregation" |
Returns the generated MongoDB aggregation pipeline, the database and collection used and a confidence score on a scale from 0 to 10 on how confident the AI is that the aggregation will answer the question correct. | confidence, database, collection, aggregation |
"result" |
Returns the raw query results from the executed aggregation. | result |
"answer" |
Returns a natural language response based on the results from the executed aggregation. | answer |
Example returning all three steps
Let's imagine the tabletennis example from the first request section once more.
With all three steps the request looks like this:
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'Who won the last match?',
returnTypes: ['aggregation', 'result', 'answer']
});And the response looks like this:
{
"database": "samples",
"collection": "tabletennis",
"aggregation": [
{ "$sort": { "year": -1, "matchInYear": -1 } },
{ "$limit": 1 },
{
"$project": {
"winner": {
"$cond": {
"if": { "$eq": ["$matchwinner", "home"] },
"then": "$players.home",
"else": "$players.away"
}
}
}
}
],
"result": [{ "_id": "67d352056d3ef0f2281524cf", "winner": "Frank" }],
"answer": "Frank won the last match. According to our records, he emerged as the winner, highlighting his strong performance in that game."
}Secure Data Separation for multi-tenant usage
You can enable secure data separation by ensuring aggregation pipelines filter data based on provided values which we call Required Inputs.
These values are added to the pipeline by the Florentine.ai transformation layer after the aggregation generation by the LLM. Thus Florentine.ai can assure each user only retrieves the data he is eligible to.
Keys are defined as Required Input in your account, please refer to the section in our official docs on how to do that.
Providing Required Inputs
Provide your Required Inputs inside a requiredInputs array with keyPath and value for each key you set as Required Input and add it to the .ask() method:
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'What is the revenue of my products this year?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'accountId',
value: '507f1f77bcf86cd799439011'
}
]
});You may also provide a database and a collections array in case you have Required Inputs with the same keyPath in multiple collections but different value for the collections:
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'Whats the current monthly rent of my tenants?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'name',
value: 'Sesame Street',
database: 'rentals',
collections: ['houses']
},
{
keyPath: 'name',
value: { $in: ['Ernie', 'Bert'] },
database: 'rentals',
collections: ['tenants']
}
]
});Required Inputs Configuration
| Field | Required | Type | Description | Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|---|
keyPath |
Yes | String | The path to the field that should be filtered. | Must be a valid key path. |
value |
Yes | Any | The value(s) to filter by (type-specific, see Supported Value Types). | Must match the field's type (String, ObjectId, Boolean, Number, or Date). |
database |
No | String | The database containing the collections to filter. | Must be provided if collections is provided. |
collections |
No | Array<String> |
The specific collections within the database to apply the filter to. | Must contain at least one collection. |
Supported Value Types
Based on the type of the values for the key you have different options on what you can provide as a Required Input value:
| Type | Format Examples | Operators Supported | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
String or Array<String> |
"text"{ $in: ["text1", "text2"] } |
$in |
Case-sensitive. |
ObjectId or Array<ObjectId> |
"507f191e810c19729de860ea"{ $in: ["507f191e810c19729de860ea", "507f191e810c19729de860eb"] } |
$in |
Provided as strings. |
Boolean |
true/false |
— | Only exact values. |
Number or Array<Number> |
42{ $gt: 10, $lte: 100 }{ $in: [1, 2, 3] }{ $in: [{$gte:1}, {$lt:10}] } |
$gt, $gte, $lt, $lte, $in |
Supports decimals. |
Date or Array<Date> |
"2024-01-01T00:00:00Z" (UTC)"2024-01-01T00:00:00-05:00"(timezone offset) |
$gt, $gte, $lt, $lte, $in |
ISO 8601 format. |
Usage Examples
Example type: String
Usecase: A user should only be able to see statistics of the players he frequently plays with.
Solution: Restricting access by player name to a group of 4 players.
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'Which player had the most wins?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'name',
value: { $in: ['Megan', 'Frank', 'Jen', 'Bob'] }
}
]
});Example type: ObjectId
Usecase: A user should only be able to see the revenue of his own products.
Solution: Restricting the access by the accountId to one specific account.
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'Whats the revenue of my products?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'accountId',
value: '507f1f77bcf86cd799439011'
}
]
});Example type: Boolean
Usecase: Every analysis of customers should only be performed on paying customers.
Solution: Restricting the access by isPaidAccount to paying customers only.
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'How many customers registered in the last year?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'isPaidAccount',
value: true
}
]
});Example type: Number
Usecase: An employee should only be allowed to see payment information for payments below a certain amount.
Solution: Restricting the access by amount to payments below 10.000.
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'List all payments we received.',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'amount',
value: { $lt: 10000 }
}
]
});Example type: Date
Usecase: The analysis of financial data should only include one specific year.
Solution: Restricting the access by transactionDate to all transactions in 2024.
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'What was our revenue, profit and margin per month?',
requiredInputs: [
{
keyPath: 'transactionDate',
value: {
$gte: '2023-01-01T00:00:00Z',
$lt: '2024-01-01T00:00:00Z'
}
}
]
});Sessions
Sessions allow Florentine.ai to enable a server-side chat history. Just provide a sessionId string like this:
const res = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'What is the revenue of my products this year?',
sessionId: '<YOUR_SESSION_ID>'
});Sessions are mandatory unless you disable the server-side chat history by setting withHistory to false inside the constructor:
const FlorentineAI = new Florentine({
florentineToken: '<FLORENTINE_API_KEY>',
withHistory: false
});[!NOTE] It is strongly recommended to use a
sessionIdto have meaningful multi-turn conversations.
Errors
All errors from the Florentine.ai API follow this consistent JSON structure:
{
"error": {
"name": "FlorentineApiError",
"statusCode": 401,
"message": "Please provide your Florentine API key. You can find it in your account settings: https://florentine.ai/settings",
"errorCode": "NO_TOKEN",
"requestId": "abc123"
}
}| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name |
string | Error class name (e.g. FlorentineApiError, FlorentineConnectionError) |
statusCode |
number | HTTP status code (e.g. 400, 500) |
message |
string | Explanation of what went wrong |
errorCode |
string | Error identifier (e.g. NO_TOKEN, INVALID_LLM_KEY) |
requestId |
string | Unique ID for this request (helpful for support and debugging) |
Handle errors in client
API errors are automatically thrown as JavaScript error classes:
import { Florentine, FlorentineApiError } from '@florentine-ai/api';
try {
const FlorentineAI = new Florentine({});
const res: TFlorentineReturnOutput = await FlorentineAI.ask({
question: 'Who is Florentine?'
});
} catch (err) {
if (err instanceof FlorentineApiError) {
console.error(err.message); // "Please provide your Florentine API key."
console.error(err.statusCode); // 401
console.error(err.errorCode); // "NO_TOKEN"
console.error(err.requestId); // "abc123"
}
}All client errors extend the FlorentineError class, so you can catch all client related errors like this:
if (err instanceof FlorentineError) {
// Catches all florentine npm package errors
}Common Errors
| Error Type | errorCode | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
FlorentineApiError |
NO_TOKEN |
The Florentine API key is missing |
FlorentineApiError |
INVALID_TOKEN |
The Florentine API key is invalid |
FlorentineApiError |
LLM_KEY_WITHOUT_SERVICE |
You must provide a llmService if llmKey is defined |
FlorentineApiError |
LLM_SERVICE_WITHOUT_KEY |
You must provide a llmKey if llmService is defined |
FlorentineApiError |
INVALID_LLM_SERVICE |
Invalid llmService provided |
FlorentineApiError |
NO_OWN_LLM_KEY |
You need to provide your own llm key |
FlorentineApiError |
NO_ACTIVE_COLLECTIONS |
No collections activated for the account |
FlorentineApiError |
MISSING_REQUIRED_INPUT |
Required input is missing |
FlorentineApiError |
INVALID_REQUIRED_INPUT |
Required input is invalid |
FlorentineApiError |
INVALID_REQUIRED_INPUT_FORMAT |
Required input format is invalid |
FlorentineApiError |
NO_QUESTION |
Question is missing |
FlorentineApiError |
EXECUTION_FAILURE |
Created aggregation execution failed |
FlorentineApiError |
NO_CHAT_ID |
History chat id required but missing |
FlorentineLLMError |
API_KEY_ISSUE |
LLM API key is invalid |
FlorentineLLMError |
NO_RETURN |
Florentine.ai did not receive a valid LLM return |
FlorentineLLMError |
RATE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED |
LLM Request size too big |
FlorentineApiError |
TOO_MANY_TOKENS |
The aggregation prompt exceeds the maximum tokens of the LLM model |
FlorentineConnectionError |
CONNECTION_REFUSED |
Could not connect to database for aggregation execution |
FlorentineCollectionError |
NO_EXECUTION |
Created aggregation could not be executed |
FlorentinePipelineError |
MODIFICATION_FAILED |
Modifying the aggregation pipeline failed |
FlorentineUsageError |
LIMIT_REACHED |
All API requests included in your plan depleted |
FlorentineUnknownError |
UNKNOWN_ERROR |
All occurring unknown errors |