Package Exports
- onelinelogger
- onelinelogger/onelinelogger.js
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (onelinelogger) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
OneLineLogger
Simple no-fuss colorised logging for NodeJS
Feature Overview
- Light-weight, quick to setup and easy to use.
- Multiple logger instances
- Customizable logger prefixes (to help distinguish logging from different modules)
- One line statement to optionally upgrade (colorize and timestamp) all existing uses of
console.log(),console.info(),console.warn()andconsole.error()throughout a code base. - Log to file.
- Configurable logging levels - DEBUG, INFO, WARN & ERROR.
Please note OneLineLogger is for NodeJS. It will not work in Web Browsers.
Installing
NPM
npm install onelineloggerGIT
Clone from GIT and install dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/garyns/OneLineLogger.git
cd OneLineLogger
npm installExamples
Basic Usage
// Variable logger is considered the 'default logger' instance. Custom loggers are discussed later.
var logger = require("onelinelogger");
logger.log("Call to logger.log()");
logger.info("Call to logger.info()");
logger.warn("Call to logger.warn()");
logger.error("Call to logger.error()");
logger.debug("Call to logger.debug()");
logger.highlight("Call to logger.highlight()");Here is the output:
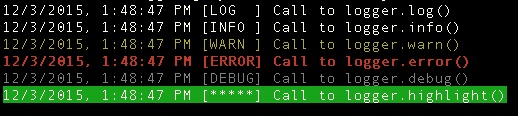
For onelinelogger 1.1.2+ logger.boo() is an alias for logger.highlight()
Overloading console.log() and related functions
var logger = require("onelinelogger");
// Before Overloading
console.log("Call to console.log()");
console.info("Call to console.info()");
console.warn("Call to console.warn()");
console.error("Call to console.error()");
// Overload with default logger
logger.replaceConsole();
console.log("Call to console.log()");
console.info("Call to console.info()");
console.warn("Call to console.warn()");
console.error("Call to console.error()");
console.debug("Call to console.debug()");
console.highlight("Call to console.highlight()");Here is the output (spacing added):
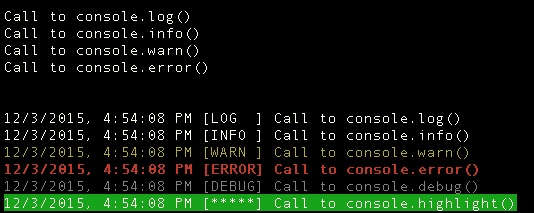
Custom Logger Instance
Create custom loggers to help associate log entries with different parts of your code.
// Default Logger instance
var logger = require("onelinelogger");
// Custom Logger instance
// [MY_LOGGER] is now added to every line
var myLogger = logger.create("MY_LOGGER");
myLogger.log("Call to myLogger.log()");
myLogger.info("Call to myLogger.info()");
myLogger.warn("Call to myLogger.warn()");
myLogger.error("Call to myLogger.error()");
myLogger.debug("Call to myLogger.debug()");
myLogger.highlight("Call to myLogger.highlight()");
// Alternatively, you could...
var myLogger2 = require("onelinelogger").create("MY_LOGGER2");
Here is the output:

You can change the 'prefix' of a logger by calling setPrefix().
var logger = require("onelinelogger");
// Output of default logger now prefixed with [MAIN]
logger.setPrefix("MAIN");
// Customer Logger - [MY_LOGGER] is added to every line...
var myLogger = logger.create("MY_LOGGER");
// ... And now it's [THEIR_LOGGER]
myLogger.setPrefix("THEIR_LOGGER");Global Settings
These settings affect ALL logger instances - that is the default logger and any custom loggers you create.
var logger = require("onelinelogger");
// Append all output to a file
logger.setGlobalFile("log.txt");
// Stop logging to a file
logger.setGlobalFile(null);
// Set the length of the prefix text
// Tweaking this property helps you keep your text lining up
// Eg 0 -> [MAIN], where 10 -> [MAIN ]
logger.setGlobalPrefixLength(10);
// Set Logging Level to one of constants logger.DEBUG logger.INFO (default), logger.NOTICE, logger.WARN or logger.ERROR, or alternatively the strings DEBUG, INFO, NOTICE, WARN or ERROR
logger.setLevel(logger.INFO)
logger.setLevel("WARN")
// Get Logging Level (as Number 0 - 4).
const currentLogLevel = logger.getLevel()
// Get Logging Level Name (DEBUG, INFO, NOTICE, WARN or ERROR)
const currentLogLevelName = logger.getLevelName()
// Suppress (false) or show (true) calls to .debug()
// NOTE deprecated in v1.1.2. Use setLevel(logger.DEBUG) instead.
logger.setGlobalDebugging(true);
// Check if log level is logger.DEBUG
const debugging = logger.isDebug();
// The previous isDebug() example is equivalent to
const debugging = logger.getLevel() === logger.DEBUG