Package Exports
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (@loopback/graphql) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
@loopback/graphql
This module provides integration with GraphQL using type-graphql.
{% include note.html content="
The @loopback/graphql module provides first-class GraphQL support in
LoopBack 4. For the general OpenAPI REST API wrapper, see
Using OpenAPI-to-GraphQL" %}
Stability: ⚠️Experimental⚠️
Experimental packages provide early access to advanced or experimental functionality to get community feedback. Such modules are published to npm using
0.x.yversions. Their APIs and functionality may be subject to breaking changes in future releases.
Installation
npm install --save @loopback/graphqlBasic Use
Let's assume we build an application to expose GraphQL endpoints similar as @loopback/example-graphql.
export class MyApplication extends BootMixin(RestApplication) {
constructor(config: ApplicationConfig) {
super(config);
this.projectRoot = __dirname;
this.component(GraphQLComponent);
this.configure(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_SERVER).to({asMiddlewareOnly: true});
}
}Configure GraphQLServer
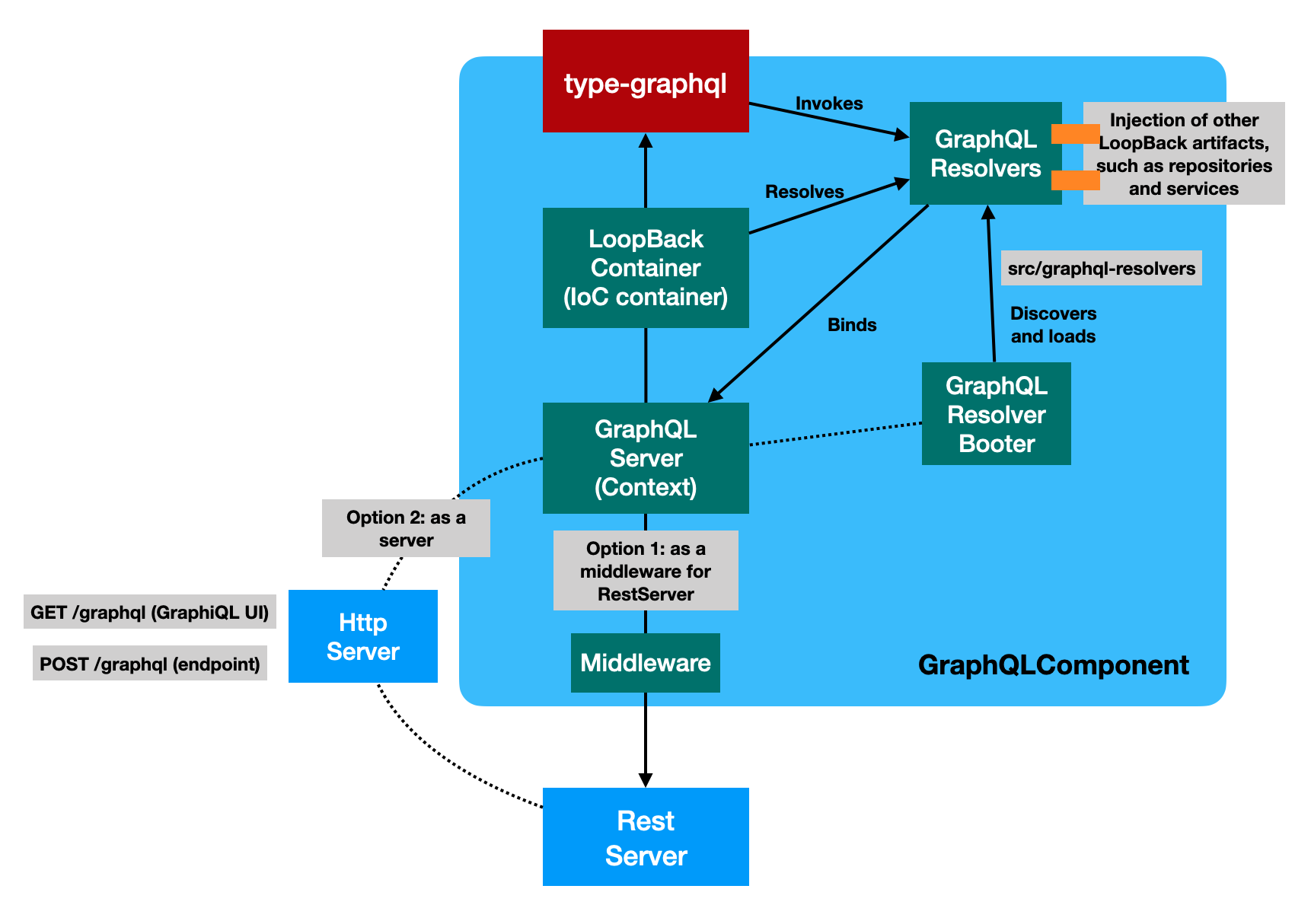
This package can be used in two flavors:
- As a server for LoopBack applications
import {Application} from '@loopback/core';
import {GraphQLServer} from '@loopback/graphql';
const app = new Application();
const serverBinding = app.server(GraphQLServer);
app.configure(serverBinding.key).to({host: '127.0.0.1', port: 0});
server = await app.getServer(GraphQLServer);
// ...
await app.start();- As a middleware for LoopBack REST applications
import {BootMixin} from '@loopback/boot';
import {RepositoryMixin} from '@loopback/repository';
import {RestApplication} from '@loopback/rest';
import {ApplicationConfig} from '@loopback/core';
import {GraphQLComponent, GraphQLBindings} from '@loopback/graphql';
export class GraphqlDemoApplication extends BootMixin(
RepositoryMixin(RestApplication),
) {
constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) {
super(options);
this.component(GraphQLComponent);
this.configure(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_SERVER).to({
asMiddlewareOnly: true,
});
const server = this.getSync(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_SERVER);
this.expressMiddleware('middleware.express.GraphQL', server.expressApp);
// ...
// Customize @loopback/boot Booter Conventions here
this.bootOptions = {
graphqlResolvers: {
// Customize ControllerBooter Conventions here
dirs: ['graphql-resolvers'],
extensions: ['.js'],
nested: true,
},
};
}
}The GraphQLServer configuration can also be passed in from the application config, such as:
const app = new Application({
graphql: {
asMiddlewareOnly: true,
},
});Add GraphQL types
The @loopback/graphql packages supports GraphQL schemas to be defined using
only classes and decorators from type-graphql.
import {Entity, model, property} from '@loopback/repository';
import {field, Float, ID, Int, objectType} from '@loopback/graphql';
@objectType({description: 'Object representing cooking recipe'})
@model({settings: {strict: false}})
export class Recipe extends Entity {
@field(type => ID)
@property({id: true})
id: string;
@field()
@property()
title: string;
@field(type => String, {
nullable: true,
deprecationReason: 'Use `description` field instead',
})
get specification(): string | undefined {
return this.description;
}
@field({
nullable: true,
description: 'The recipe description with preparation info',
})
@property()
description?: string;
@field(type => [Int])
ratings: number[];
@field()
@property()
creationDate: Date;
@field(type => Int)
protected numberInCollection: number;
@field(type => Int)
ratingsCount: number;
@field(type => [String])
ingredients: string[];
@field(type => Int)
protected get ingredientsLength(): number {
return this.ingredients.length;
}
@field(type => Float, {nullable: true})
get averageRating(): number | null {
const ratingsCount = this.ratings.length;
if (ratingsCount === 0) {
return null;
}
const ratingsSum = this.ratings.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0);
return ratingsSum / ratingsCount;
}
}Please note that we also use @model and property decorators to define how
the entities being persisted with LoopBack repositories.
Add GraphQL resolver classes
To serve GraphQL, an application will provide resolver classes to group query/mutation/resolver functions, similarly as how REST API endpoints are exposed via controller classes.
We use TypeScript decorators to provide metadata about individual resolvers. See type-graphql docs for more details.
Let's add recipe-resolver.ts to src/graphql-resolvers so that it can be
automatically discovered and loaded by the @loopback/graphql component.
Please note that we re-export type-graphql decorators as camel case variants,
such as query instead of Query. It's recommended that your applications
import such decorators from @loopback/graphql.
import {service} from '@loopback/core';
import {repository} from '@loopback/repository';
import {
arg,
fieldResolver,
Int,
mutation,
query,
resolver,
root,
ResolverInterface,
} from '@loopback/graphql';
import {RecipeInput} from '../graphql-types/recipe-input';
import {Recipe} from '../graphql-types/recipe-type';
import {RecipeRepository} from '../repositories';
import {RecipeService} from '../services/recipe.service';
@resolver(of => Recipe)
export class RecipeResolver implements ResolverInterface<Recipe> {
constructor(
// Inject an instance of RecipeRepository
@repository('RecipeRepository')
private readonly recipeRepo: RecipeRepository,
// Inject an instance of RecipeService
@service(RecipeService) private readonly recipeService: RecipeService,
) {}
// Map to a GraphQL query to get recipe by id
@query(returns => Recipe, {nullable: true})
async recipe(@arg('recipeId') recipeId: string) {
return this.recipeRepo.getOne(recipeId);
}
// Map to a GraphQL query to list all recipes
@query(returns => [Recipe])
async recipes(): Promise<Recipe[]> {
return this.recipeRepo.getAll();
}
// Map to a GraphQL mutation to add a new recipe
@mutation(returns => Recipe)
async addRecipe(@arg('recipe') recipe: RecipeInput): Promise<Recipe> {
return this.recipeRepo.add(recipe);
}
// Map to a calculated GraphQL field - `numberInCollection`
@fieldResolver()
async numberInCollection(@root() recipe: Recipe): Promise<number> {
const index = await this.recipeRepo.findIndex(recipe);
return index + 1;
}
// Map to a calculated GraphQL field - `ratingsCount`
@fieldResolver()
ratingsCount(
@root() recipe: Recipe,
@arg('minRate', type => Int, {defaultValue: 0.0})
minRate: number,
): number {
return this.recipeService.ratingsCount(recipe, minRate);
}
}Use LoopBack dependency injections in resolver classes
All of LoopBack decorators for dependency injection , such as @inject,
@service, @repository, and @config, can be used with resolver classes.
import {service} from '@loopback/core';
@resolver(of => Recipe)
export class RecipeResolver implements ResolverInterface<Recipe> {
constructor(
// constructor injection of service
@repository('RecipeRepository')
private readonly recipeRepo: RecipeRepository,
@service(RecipeService) private readonly recipeService: RecipeService,
// It's possible to inject the resolver data
@inject(GraphQLBindings.RESOLVER_DATA) private resolverData: ResolverData,
) {}
}Discover and load GraphQL resolvers
The GraphQLComponent contributes a booter that discovers and registers
resolver classes from src/graphql-resolvers during app.boot().
Propagate context data
The GraphQLServer allows you to propagate context from Express to resolvers.
Register a GraphQL context resolver
The GraphQL context object can be built/enhanced by the context resolver. The
original value is {req: Request, res: Response} that represents the Express
request and response object.
export class GraphqlDemoApplication extends BootMixin(
RepositoryMixin(RestApplication),
) {
constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) {
super(options);
// ...
// It's possible to register a graphql context resolver
this.bind(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_CONTEXT_RESOLVER).to(context => {
// Add your custom logic here to produce a context from incoming ExpressContext
return {...context};
});
}
// ...
}Access the GraphQL context inside a resolver
@resolver(of => Recipe)
export class RecipeResolver implements ResolverInterface<Recipe> {
constructor(
// constructor injection of service
@repository('RecipeRepository')
private readonly recipeRepo: RecipeRepository,
@service(RecipeService) private readonly recipeService: RecipeService,
// It's possible to inject the resolver data
@inject(GraphQLBindings.RESOLVER_DATA) private resolverData: ResolverData,
) {
// `this.resolverData.context` is the GraphQL context
}
// ...
}Set up authorization checker
We can customize the authChecker for
TypeGraphQL Authorization.
export class GraphqlDemoApplication extends BootMixin(
RepositoryMixin(RestApplication),
) {
constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) {
super(options);
// ...
// It's possible to register a graphql auth checker
this.bind(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_AUTH_CHECKER).to(
(resolverData, roles) => {
// Use resolverData and roles for authorization
return true;
},
);
}
// ...
}The resolver classes and graphql types can be decorated with @authorized to
enforce authorization.
@resolver(of => Recipe)
export class RecipeResolver implements ResolverInterface<Recipe> {
constructor() {} // ...
@query(returns => Recipe, {nullable: true})
@authorized('owner') // Authorized against `owner` role
async recipe(@arg('recipeId') recipeId: string) {
return this.recipeRepo.getOne(recipeId);
}
}Register GraphQL middleware
We can register one or more TypeGraphQL Middleware as follows:
export class GraphqlDemoApplication extends BootMixin(
RepositoryMixin(RestApplication),
) {
constructor(options: ApplicationConfig = {}) {
super(options);
const server = this.getSync(GraphQLBindings.GRAPHQL_SERVER);
this.expressMiddleware('middleware.express.GraphQL', server.expressApp);
// Register a GraphQL middleware
server.middleware((resolverData, next) => {
// It's invoked for each field resolver, query and mutation operations
return next();
});
}
}Export GraphQL Schema as a file
Exporting the generated GraphQL schema file can be done by calling
exportGraphQLSchema on the GraphQLServer:
import {Application} from '@loopback/core';
import {GraphQLServer} from '@loopback/graphql';
const app = new Application();
const serverBinding = app.server(GraphQLServer);
app.configure(serverBinding.key).to({host: '127.0.0.1', port: 0});
server = await app.getServer(GraphQLServer);
// set up your resolvers
await server.exportGraphQLSchema(pathToFile);For applications using GraphQLComponent to discover resolvers, exporting the
schema file is similar to exportOpenApiSpec on RestServer:
// export-graphql-schema.ts, sibling to application.ts
import {MyApplication, MyApplicationConfig} from './application';
async function exportGraphQLSchema(): Promise<void> {
const config: MyApplicationConfig = {
rest: {
port: +(process.env.PORT ?? 3000),
host: process.env.HOST ?? 'localhost',
},
};
const outFile = process.argv[2] ?? '';
const app = new MyApplication(config);
await app.boot();
const server = await app.getServer(GraphQLServer);
await server.exportGraphQLSchema(outFile);
}
exportGraphQLSchema().catch(err => {
console.error('Fail to export GraphQL spec from the application.', err);
process.exit(1);
});Try it out
Check out @loopback/example-graphql.
Contributions
Tests
Run npm test from the root folder.
Contributors
See all contributors.
License
MIT