Package Exports
- bulbo
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (bulbo) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
bulbo v2.2.0 


Streaming static site generator, based on gulp
Install
npm install --save-dev bulboUsage
First you need to set up bulbofile.js like the following.
var asset = require('bulbo').asset
var through = require('through')
var browserify = require('browserify')
var frontMatter = require('gulp-front-matter')
var wrap = require('gulp-wrap')
asset('source/**/*.js', {read: false})(function (src) {
return src.pipe(through(function (file) {
file.contents = browserify(file.path).bundle()
this.queue(file)
}));
})
asset('source/**/*.css')
asset('source/*.html')(function (src) {
return src
.pipe(frontMatter())
.pipe(wrap(function (data) {
return fs.readFileSync('source/layouts/' + data.file.frontMatter.layout).toString()
}));
})
asset(['source/**/*', '!source/**/*.{js,css,html,lodash}'])And then the following command starts the server.
bulbo serveAnd the following builds all the given assets and saves them to build/ directory.
bulbo buildAPI
var bulbo = require('bulbo')bulbo.asset(glob, opts)
- @param {String|String[]} glob The glob pattern(s)
- @param {Object} [opts] The options
- @param {String} [opts.base] The base path.
- @param {String|String[]} [opts.watch] The glob(s) to watch (optional)
- @param {Object} [opts.watchOpts] The options to pass to watcher (optional)
This registers the glob pattern as the asset source.
Example:
bulbo.asset('src/js/**/*.js')opts.watch is used for specifying the watching path. If nothing's give, bulbo automatically watches the same path as the asset glob. So this is useful when the asset entry points and the actual source files are different.
opts.watchOpts is passed directly to the watcher (actually chokidar) as its options.
Example:
bulbo.asset('src/js/pages/*.js', {
watch: 'src/js/**/*.js' // Watches all js files under `src/js`, though build entry poits are only js files under `src/js/pages`.
})(function (src) {
return src.pipe(through(file => {
file.contents = browserify(file.path).bundle()
}))opts.base used for changing the base path of the glob pattern(s).
Example:
bulbo.asset('src/img/**/*.*') // `src/img/foo.png` is copied to `build/foo.png`
bulbo.asset('src/img/**/*.*', {base: 'src'}) // but in this case, copied to `build/img/foo.png`bulbo.asset(glob, opts)(modifier)
- @param {Function} modifier The asset modifier
This registers the asset modifier for the asset. The modifier is called with the paramter of source file (vinyl type) stream and must return a transformed stream. It throws exception if the modifier does not return a readable stream.
Because the stream which is passed to modifier is vinyl stream, which is the same as gulp.src(glob) in gulp, you can use any gulp-plugins or gulp compatible stream processors for passing through it.
Example:
bulbo.asset('src/js/**/*.js')(function (src) {
return src.pipe(through(function (file) {
file.contents = browserify(file.path).bundle()
this.queue(file)
}))
})bulbo.dest(path)
- @param {String} path
This sets the build destination. (The default is build)
Example:
bulbo.dest('dist')bulbo.port(port)
- @param {Number} port
This sets the port number of the asset server. (The default is 7100.)
Example:
bulbo.port(7500)Commands
npm install -g bulbo installs command bulbo. Which supports 2 subcommands build and serve.
bulbo build
This builds all the registered assets into the destination directory. The defualt destination is build. The path is configurable by bulbo.dest(path) in bulbofile.
bulbo serve
This starts the local server which serves all the registered assets on it. The default port is 7100. The number is configurable by bulbo.port(number) in bulbofile.
bulbo command without arguments also does the same as bulbo serve. You can just simply call bulbo to start bulbo server.
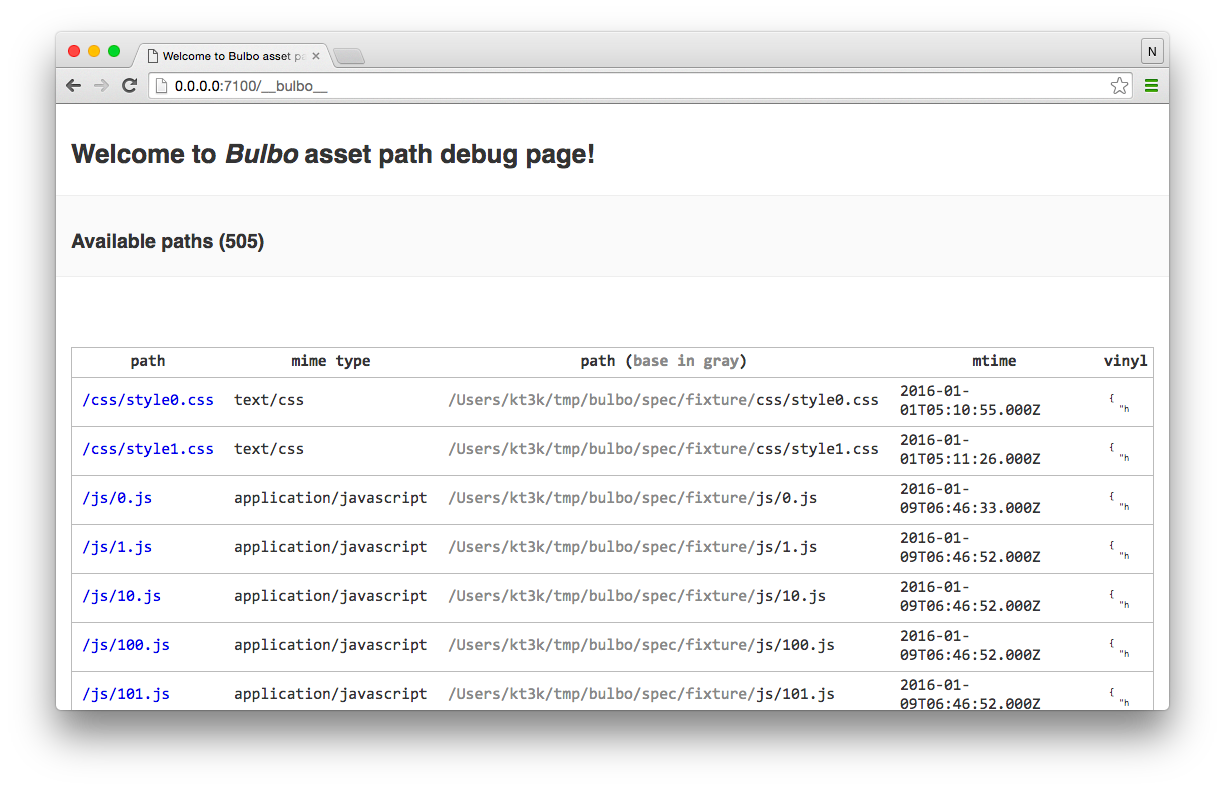
The bulbo server has builtin debug url at 0.0.0.0:7100/__bulbo__. You can find there all the available paths (assets) on the server. It's useful for debugging the asset stream.
Recipes
Use es6 in bulbo file
Bulbo uses js-liftoff under the hood, which means you can enable es6 syntax by renaming bulbofile.js to bulbofile.babel.js and adding babel-register dependency.
npm install --save-dev babel-registerYou also need to set up .babelrc or babel config in package.json to use es6 in bulbo.babel.js.
Uglify scripts only when it's production build
Use gulp-if:
import gulpif from 'gulp-if'
import uglify from 'gulp-uglify'
const PRODUCTION_BUILD = process.NODE_ENV === 'production'
asset('source/**/*.js')(src => src
.pipe(gulpif(PRODUCTION_BUILD, uglify()))This uglifies the scripts only when the variable NODE_ENV is 'production'.
Or alternatively use through or through2:
import through from 'through'
import uglify from 'gulp-uglify'
const PRODUCTION_BUILD = process.NODE_ENV === 'production'
asset('source/**/*.js')(src => src
.pipe(PRODUCTION_BUILD ? uglify() : through()))Want to render my contents with template engine XXXX
Use gulp-wrap and the engine option:
import wrap from 'gulp-wrap'
import frontMatter from 'gulp-front-matter'
asset('source/**/*.html')(src => src
.pipe(frontMatter())
.pipe(wrap({src: 'source/layout.nunjucks'}, null, {engine: 'nunjucks'})))Note You need to npm install nunjucks in this case.
This example wraps your html in the nunjucks template. The contents of each html file is refereced by contents and the front matter by file.frontMatter.
Watch different paths from source path.
Use watch option in the asset options.
asset('source/page/*.js', {watch: 'source/**/*.js'})This is useful when the entrypoints of the asset and the actual source files are different. For example, if you use browserify to bunble your scripts, your entrypoints are bundle's entrypoit files but you need to watch all of your source files which form the bundles.
License
MIT
Release history
- 2016-01-09 v1.0.2 Improved server start time.
- 2016-01-08 v1.0.1 Fixed build file number limit bug.
- 2016-01-03 v1.0.0 Initial release.