Package Exports
- c-promise2
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (c-promise2) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
Table of contents
- SYNOPSIS
- Why
- Features
- Installation
- Comparison table
- Examples:
- Signals handling
- Using generators
- Atomic sub-chains
- Using decorators
- Events
thenmethod behavior notes- Related projects
- API Reference
- License
SYNOPSIS ✨
CPromise library provides an advanced version of the built-in Promise by subclassing. You might be interested in using it if you need:
- cancel the promise through rejection (including nested)
- cancel async tasks inside React components (useful to cancel internal code when components unmounts)
- with built-in decorators for class components
- with
useAsyncEffect&useAsyncCallbackhooks provided by useAsyncEffect2 package
- cancel network requests with promises, which allows the network request to be automatically aborted when the parent async function is canceled:
- control cancellation flow to write really complicated async flows with cancelation ability.
- define atomic promise chains that cannot be canceled in the middle of execution from upper chains
AbortControllersupport for promises- some way to make cancellation declarative (with method decorators)
- capture promise chain progress with defining progress impact for each promise (default 1)
- generators support to write a flat code in the same way as
async&awaitdo, but withCPromisefeatures support - pause/resume the promise
- pending timeout
- concurrent limitation for
allandallSettledmethods withmapperreducer - advanced signal communication
In terms of the library the cancellation means rejection with a special error subclass.
import { CPromise } from "c-promise2";
const promise= new CPromise((resolve, reject, {onCancel, onPause, onResume})=>{
onCancel(()=>{
//optionally some code here to abort your long-term task (abort request, stop timers etc.)
});
}).then(
value => console.log(`Done: ${value}`),
(err, scope) => {
console.warn(`Failed: ${err}`); // Failed: CanceledError: canceled
console.log('chain isCanceled:', promise.isCanceled); // true
console.log('promise isCanceled:', scope.isCanceled); // true
}
);
console.log('isPromise:', promise instanceof Promise); // true
setTimeout(()=> promise.cancel(), 1000);Log:
isPromise: true
Failed: CanceledError: canceled
chain isCanceled: true
promise isCanceled: trueCPromise fully supports writing "flat" cancellable code:
const p= CPromise.run(function*(){
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
return 1;
}).then(function*(v){
for(let i=0; i<3; i++) {
console.log(`delay [${i}]`);
yield CPromise.delay(500);
}
return v + 2;
}).then(v=> console.log(`Done: ${v}`));
//setTimeout(()=> p.cancel(), 1000);You can use decorators to cancel asynchronous tasks inside React components when unmounted, thereby preventing the well-known React leak warning from appearing:
export class FetchComponent extends React.Component {
state = {text: ""};
@timeout(5000)
@listen
@async
*componentDidMount() {
const response = yield cpFetch(this.props.url);
this.setState({ text: `json: ${yield response.text()}` });
}
render() {
return <div>{this.state.text}</div>;
}
@cancel()
componentWillUnmount() {}
}Why ❓
You may run into a problem when you need to cancel some long-term asynchronous operation before it will be completed with success or failure, just because the result has lost its relevance to you.
Features
- no dependencies (except [native] Promise)
- built-in
AbortControllerclass - browser support
- supports two ways to make your promise internal code cancellable:
onCancelcallbacks (clear timers, abort requests)signalprovided by the AbortController (to wrap API like fetch method)
- 🔥 supports cancellation of the whole chain
- 🔥 supports generator to CPromise resolving (something similar like co library does);
- 🔥 progress capturing support
- 🔥 pretty awesome isomorphic decorators, with both specification support
CPromise.allsupports concurrency limitCPromise.allandCPromise.racemethods have cancellation support, so the others nested pending promises will be canceled when the resulting promise settled- promise suspending (using
pauseandresumemethods) - custom signals (
emitSignal) delaymethod to return a promise that will be resolved with the value after a timeout- ability to set the
weightfor each promise in the chain to manage the impact on chain progress - ability to attach meta info on each set of the progress
catchmethod supports error class filtering- Supports listening to multiple
AbortControllersignals
Installation 🔨
- Install for node.js using npm/yarn:
$ npm install c-promise2$ yarn add c-promise2The package consists of pre-built umd, cjs, mjs bundles which can be found in the ./dist/ directory
- Import the library:
import {CPromise} from "c-promise2";
// const {CPromise} = require("c-promise2"); // using require
// import {CPromise} from "c-promise2/dev"; // development version
const chain= CPromise.delay(1000, 'It works!').then(message => console.log('Done', message));
//chain.cancel();As an alternative you can use any CDN with npm support:
production UMD version (or minified ~9KB) - provides the CPromise class as the default export, other exports values declared as static properties
Comparison table
| CPromise | BlueBird.js | p-cancelable | |
|---|---|---|---|
.cancel() is synchronous |
❌* (.cancel emits a cancel signal synchronously, but the cancellation is asynchronous) | ✓ | ✓ |
| No setup code required to make cancellation work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Cancellation type | asynchronous, rejection with CanceledError follows the special algorithm |
synchronous (ignoring attached callbacks) | synchronous (ignoring attached callbacks) / asynchronous (rejecting) |
| onCancel handler to clean up internal tasks | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Atomic sub-chains (protected from cancellation by upper chains) | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Cancellation flows | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Custom cancellation reasons | ✓ | ❌ | ✓ |
Cancellation composes with other own features, like .all, .race, .allSettled |
✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| Chaining/nested promise cancellation support | ✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| Generators support for “flat” coroutines (as a functional replacement for ECMA async functions) | ✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| Coroutines cancellation | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Concurrency limitation | ✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| Signals/data flows | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Chain progress capturing | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Pause/resume support | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| timeouts | ✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| AbortController support (outer/inner) | ✓/✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
.catch errors filter |
✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
.delay helper |
✓ | ✓ | ❌ |
| ECMA decorators for methods (legacy/current) | ✓/✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Inherited from the native Promise | ✓ | ❌ | ❌ |
Examples
Progress capturing and cancellation
Basic example (Live demo):
import CPromise from 'c-promise';
const delay= (ms, value)=>{
return new CPromise((resolve, reject, {onCancel}) => {
const timer = setTimeout(resolve, ms, value);
onCancel(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
console.log('clear timeout');
}) // clear internal operations on 'cancel' event
})
}
const promise = CPromise.all([
delay(1000, 'a'),
delay(2000, 'b'),
delay(3000, 'c'),
delay(4000, 'd'),
delay(5000, 'e'),
])
.progress(value=> console.log(`Progress: ${(value * 100).toFixed(1)}%`));
console.log('isPromise:', promise instanceof Promise); // true
(async()=>{
try {
console.log(`Done: `, await promise);
}catch(err){
console.warn(`Failed: ${err}`);
console.log('isCanceled:', promise.isCanceled);
}
})()
setTimeout(()=> promise.cancel(), 3100); // cancel the promise after 3100msConsole output:
isPromise: true
Progress: 20.0%
Progress: 40.0%
Progress: 60.0%
clear timeout
clear timeout
isCanceled: true
Failed: CanceledError: canceled
Process finished with exit code 0Pause / resume promises
See the live demo
import CPromise from 'c-promise';
function cancelableDelay(ms, value){
return new CPromise(function(resolve, reject, {onCancel, onPause, onResume}){
let timestamp= Date.now();
let timeLeft;
let timer= setTimeout(resolve, ms, value);
onPause(()=>{
console.log(`Pause`);
clearTimeout(timer);
timer=0;
timeLeft= ms - (Date.now()- timestamp);
timestamp= Date.now();
});
onResume(()=>{
console.log(`Resume`);
timer= setTimeout(resolve, timeLeft, value);
});
onCancel(()=>{
console.log(`Cancel`);
timer && clearTimeout(timer);
})
});
}
const chain= cancelableDelay(1000, 123)
.then(
value=> console.log(`Done:`, value),
err=> console.warn(`Fail: ${err}`)
);
setTimeout(()=>{
chain.pause();
setTimeout(()=>{
chain.resume();
}, 5000);
}, 100);
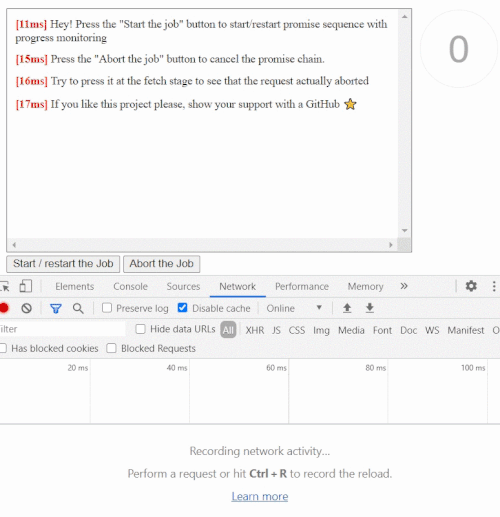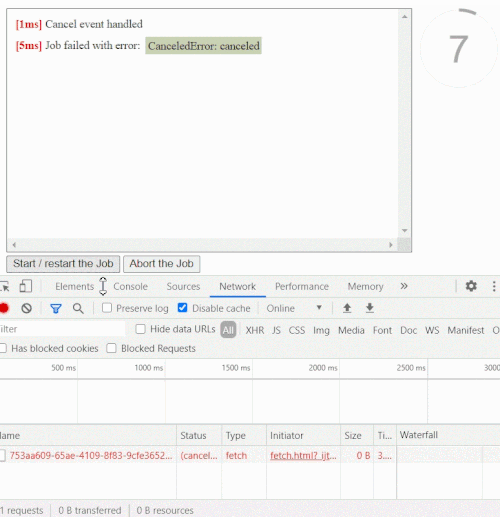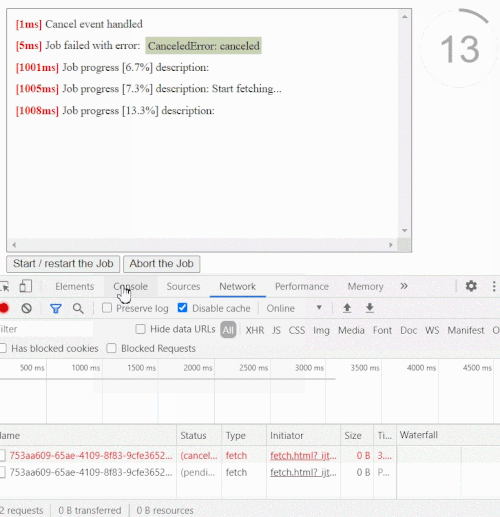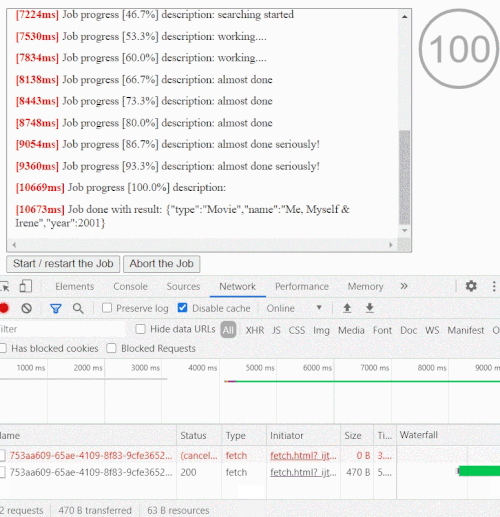
Abortable fetch with timeout
This is how an abortable fetch (live example) with a timeout might look like
function fetchWithTimeout(url, {timeout, ...fetchOptions}= {}) {
return new CPromise((resolve, reject, {signal}) => {
fetch(url, {...fetchOptions, signal}).then(resolve, reject)
}, {timeout, nativeController: true})
}
const promise= fetchWithTimeout('http://localhost/', {timeout: 5000})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(`Done: `, data), err => console.log(`Error: `, err))
setTimeout(()=> promise.cancel(), 1000);
// you able to call cancel() at any time to cancel the entire chain at any stage
// the related network request will also be abortedYou can use the cp-fetch package which provides a ready to use CPromise wrapper for cross-platform fetch API.
Wrapping axios request
function cancelableAxios(url){
return new CPromise((resolve, reject, {onCancel})=>{
axios.get(url, {
cancelToken: new axios.CancelToken(function executor(cancel) {
onCancel(cancel)
})
}).then(resolve, reject);
});
}Tip: You can use ready for use cp-axios package for this.
Concurrency limitation:
import CPromise from "c-promise2";
import cpFetch from "cp-fetch";
(async()=>{
await CPromise.all([
'url1',
'url2',
'url3',
'url4',
'url5',
'url6',
], {
mapper: async (url) => {
return cpFetch(url);
},
concurrency: 2
})
console.log('Done');
});
// Or
(async()=>{
await CPromise.all(function*(){
const urls= [
'url1',
'url2',
'url3',
'url4',
'url5',
'url6',
];
for(let url of urls){
yield cpFetch('url1');
}
}, {
concurrency: 2
})
console.log('Done');
})();Retrying async operations
Use CPromise.retry to retry async operations (3 attempts by default) with a delay(by default delay = attempt * 1000ms)
const p= CPromise.retry(function*(scope, attempt){
console.log(`attempt [${attempt}]`);
this.innerWeight(3);
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
throw Error('oops');
}).progress((v) => {
console.log(`Progress: ${v}`);
});
// setTimeout(() => p.cancel(), 5000); stop tryingconst p= CPromise.retry(async function(attempt){
console.log(`attempt [${attempt}]`);
await CPromise.delay(1000);
await CPromise.delay(1000);
await CPromise.delay(1000);
throw Error('oops');
}).progress((v) => {
console.log(`Progress: ${v}`);
});You can use .cancel / .pause / .resume to control the sequence of attempts.
Using with React
React class component
Check out this live demo
import CPromise from "c-promise2";
import cFetch from "cp-fetch";
export class AsyncComponent extends React.Component {
state = {};
async componentDidMount() {
console.log("mounted");
this.controller = new CPromise.AbortController();
try {
const json = await this.myAsyncTask(
"https://run.mocky.io/v3/7b038025-fc5f-4564-90eb-4373f0721822"
);
console.log("json:", json);
await this.myAsyncTaskWithDelay(1000, 123); // just another async task
this.setState({ text: JSON.stringify(json) });
} catch (err) {
if (CPromise.isCanceledError(err)) {
console.log("tasks terminated");
}
}
}
myAsyncTask(url) {
return CPromise.from(function* () {
const response = yield cFetch(url); // cancellable request
// some another promises here
return yield response.json();
}).listen(this.controller.signal);
}
// another one cancellable async task
myAsyncTaskWithDelay(ms, value) {
return new CPromise((resolve, reject, { onCancel }) => {
const timer = setTimeout(resolve, ms, value);
onCancel(() => {
console.log("timeout cleared");
clearTimeout(timer);
});
}).listen(this.controller.signal);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
AsyncComponent: <span>{this.state.text}</span>
</div>
);
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("unmounted");
this.controller.abort(); // kill all tasks
}
}React functional component
Using hooks and CPromise cancel method Live Demo:
import React, { useEffect, useState } from "react";
import { CPromise, CanceledError } from "c-promise2";
import cpFetch from "cp-fetch";
function MyComponent(props) {
const [text, setText] = useState("fetching...");
useEffect(() => {
console.log("mount");
const promise = CPromise.from(function* () {
try {
const response = yield cpFetch(props.url);
const json = yield response.json();
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
setText(`Success: ${JSON.stringify(json)}`);
} catch (err) {
console.warn(err);
CanceledError.rethrow(err);
setText(`Failed: ${err}`);
}
});
return () => {
console.log("unmount");
promise.cancel();
};
}, [props.url]);
return <p>{text}</p>;
}React class component with CPromise decorators
With CPromise decorators, a generic React class component might look like this one: Demo
import React from "react";
import "bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css";
import "./styles.css";
import { async, listen, cancel, timeout } from "c-promise2";
import cpFetch from "cp-fetch";
export class TestComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
text: ""
};
@timeout(5000)
@listen
@async
*componentDidMount() {
console.log("mounted");
const response = yield cpFetch(this.props.url);
this.setState({ text: `json: ${yield response.text()}` });
}
render() {
return <div>{this.state.text}</div>;
}
@cancel()
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("unmounted");
}
}It automatically manages async code i.g request, so it protects from warning appearing like:
Warning: Can’t perform a React state update on an unmounted component.
More complex example: Demo
import React from "react";
import {
CPromise,
async,
listen,
cancel,
timeout,
canceled,
E_REASON_DISPOSED
} from "c-promise2";
import cpFetch from "cp-fetch";
export class TestComponent extends React.Component {
state = {};
@canceled(function (err) {
console.warn(`Canceled: ${err}`);
if (err.code !== E_REASON_DISPOSED) {
this.setState({ text: err + "" });
}
})
@listen
@async
*componentDidMount() {
console.log("mounted");
const json = yield this.fetchJSON(
"https://run.mocky.io/v3/7b038025-fc5f-4564-90eb-4373f0721822?mocky-delay=2s"
);
this.setState({ text: JSON.stringify(json) });
}
@timeout(5000)
@async
*fetchJSON(url) {
const response = yield cpFetch(url); // cancellable request
return yield response.json();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
AsyncComponent: <span>{this.state.text || "fetching..."}</span>
</div>
);
}
@cancel(E_REASON_DISPOSED)
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("unmounted");
}
}Signals handling
Every CPromise instance can handle "signals", emitted using emitSignal method.
The method emits a signal event on each pending promise in the chain until some handler returns true as the result.
This method is used internally for predefined system signals for cancellation and suspending actions.
const CPromise= require('../lib/c-promise');
const chain= new CPromise((resolve, reject, scope)=>{
scope.on('signal', (type, data) => {
if (type === 'inc') { // ignore other signal types
console.log(`Signal ${type} handled`);
resolve(data.x + 1);
return true; // we have accepted this signal, so we should return `true` to stop the propagation
}
});
}).then(
(value)=> console.log(`Done: ${value}`),
(err)=> console.log(`Failed: ${err}`)
)
setTimeout(() => {
// returns true
console.log(`Inc signal result: ${chain.emitSignal('inc', {x: 2})}`);
// returns false because there are no handlers to catch this signal type
console.log(`Custom signal result: ${chain.emitSignal('custom')}`);
});Console output:
Signal inc handled
Inc signal result: true
Custom signal result: false
Done: 3
Process finished with exit code 0There are the following system signals (just for reference, don't use them unless you know what you are doing):
CPromise.SIGNAL_CANCELCPromise.SIGNAL_PAUSECPromise.SIGNAL_RESUME
Using Generators as an alternative of ECMA async functions
Generally, you able to use CPromise with ES6 async functions,
but if you need some specific functionality such as progress capturing or cancellation,
you need to use generators instead of async functions to make it work.
This is because the async function leads all the nested thenables into its own Promise class,
and there is nothing we can do about it. Generators allow you to write asynchronous code
just in the same way as async functions do, just use yield instead of await.
See the live demo
import CPromise from "c-promise2";
const promise= CPromise.from(function*(){
this.innerWeight(12); //optionally set the expected internal progress score of the nested chain
yield CPromise.delay(1000);
yield [CPromise.delay(1000), CPromise.delay(1500)] // resolve chains using CPromise.all([...chains]);
yield [[CPromise.delay(1000), CPromise.delay(1500)]] // resolve chains using CPromise.race([...chains]);
yield new Promise.resolve(); // any thenable object will be resolved
return "It works!";
})
.progress(value=> console.log(`Progress: ${value}`))
.then(message=> console.log(`Done: ${message}`));Then method also supports generators as callback function
CPromise.resolve().then(function*(){
const value1= yield CPromise.delay(3000, 3);
// Run promises in parallel using CPromise.all (shortcut syntax)
const [value2, value3]= yield [CPromise.delay(3000, 4), CPromise.delay(3000, 5)]
return value1 + value2 + value3;
}).then(value=>{
console.log(`Done: ${value}`); // Done: 12
}, err=>{
console.log(`Failed: ${err}`);
})Atomic sub-chains
Sometimes you need to prevent any sub-chain from being canceled from the outside because you want to allow some
already started asynchronous procedure to be completed before closing the following promise chains.
To solve this challenge use .atomic(["disabled"|"detached"|"await"]) method.
'detached'- keep the sub-chain execution running in 'background', the main chain reject immediately'await'- wait for the sub-chain to complete and then reject the next promise in the outer chainfalseconsidering as'disabled'trueconsidering as'await'
Check out the difference with examples:
Normal cancellation behaviour .atomic('disabled') (Demo):
const p = CPromise.delay(1000, 1)
.then((v) => {
console.log("p1");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 2);
})
.then((v) => {
console.log("p2");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 3);
})
.atomic()
.then((v) => {
console.log("p3");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 4);
})
.then(
(value) => console.log(`Done:`, value),
(err) => console.warn(`Fail: ${err}`)
);
setTimeout(() => p.cancel(), 1500);output:
p1
Fail: CanceledError: canceled
Process finished with exit code 0.atomic('detached') cancellation behaviour (Demo):
const p = CPromise.delay(1000, 1)
.then((v) => {
console.log("p1");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 2);
})
.then((v) => {
console.log("p2");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 3);
})
.atomic('detached')
.then((v) => {
console.log("p3");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 4);
})
.then(
(value) => console.log(`Done:`, value),
(err) => console.warn(`Fail: ${err}`)
);
setTimeout(() => p.cancel(), 1500);output:
p1
Fail: CanceledError: canceled
p2.atomic('await') cancellation behaviour (Demo):
const p = CPromise.delay(1000, 1)
.then((v) => {
console.log("p1");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 2);
})
.then((v) => {
console.log("p2");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 3);
})
.atomic()
.then((v) => {
console.log("p3");
return CPromise.delay(1000, 4);
})
.then(
(value) => console.log(`Done:`, value),
(err) => console.warn(`Fail: ${err}`)
);
setTimeout(() => p.cancel(), 1500);output:
p1
p2
Fail: CanceledError: canceled
Process finished with exit code 0Using decorators
The library supports a few types of decorators to make your code cleaner.
All decorators are isomorphic- @async and @async() are totally equal.
Also, they support both current and legacy decorator's specification.
@async([{timeout?: Number, innerWeight?: Number, label? : String, weight?: Number}])
Wraps a generator function into an async function, that returns CPromise instance.
import CPromise from 'c-promise2';
const {async}= CPromise;
class Test{
@async
*asyncMethod(x, y){
const z= yield CPromise.delay(1000);
return x + y + z;
}
}
const test= new Test();
const promise= test.asyncMethod(1, 2);
console.log(promise instanceof CPromise); // true
promise.then(value=> console.log(`Done: ${value}`), err=> console.warn(`Fail: ${err}`));
setTimeout(()=> promise.cancel(), 500);@listen([signal: AbortSignal|String|Symbol])
Subscribe the CPromise async function to the AbortController signal. If the first argument is String or Symbol it will be considered as controller id, created internally in context of the class. If this argument not specified or null, the internal default AbortController will be used.
@cancel([reason: String], [signal: AbortSignal|String|Symbol])
Emits the cancel signal before the target function invoking.
@canceled([onRejected(err, scope, context): Function])
Catches rejections with CanceledError errors
import cpFetch from "cpFetch";
class Test{
constructor(url) {
this.fetchJSON(url).then(json=>{
this.json= json;
// working with json;
})
}
@timeout(10000)
@listen
@async
*fetchJSON(url){
const response= yield cpFetch(url);
return yield response.json();
}
@cancel(E_REASON_DISPOSED)
destroy(){
// your code here
}
}@progress(handler: Function)
Adds a listener to monitor the function progress
class Test{
@progress(function (value, scope, data, context) {
console.log(`Progress: ${value}`);
// Prints: 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1
})
@innerWeight(4)
@async
* asyncMethod() {
yield delay(100);
yield delay(100);
yield delay(100);
yield delay(100);
}
}
const test= new Test();
const promise= test.asyncMethod();@timeout(ms: Number)
Sets the timeout option for the CPromise async function.
@innerWeight(weight: Number)
Sets the innerWeight option for the CPromise async function.
@label(label: String)
Sets the label option for the CPromise async function.
Events
All events (system and user defined) can be fired only when promises in pending state.
Predefined (system) events:
cancel(reason: CanceledError)- fired when promise is canceled (rejected withCanceledError)pause- on promise pause requestresume- on promise resume requestcapture(scope: CPromise)- fired when some consumer directly or above standing in the chain starts progress capturingprogress(value: Number, scope: CPromise, data: Object?)- fired when promise chain progress changes
Event listener attaching shortcuts (methods binded to the promise instance):
onCancel(listener: Function)onPause(listener: Function)onResume(listener: Function)onCapture(listener: Function)
then method behavior notes
The behavior of the method is slightly different from native Promise. In the case when you cancel the chain after it has been resolved within one eventloop tick, onRejected will be called with a CanceledError instance, instead of onFulfilled. This prevents the execution of unwanted code in the next eventloop tick if the user canceled the promise immediately after the promise was resolved, during the same eventloop tick.
Related projects
- cp-axios - a simple axios wrapper that provides an advanced cancellation api
- cp-fetch - fetch with timeouts and request cancellation
- use-async-effect2 - cancel async code in functional React components
API Reference
Cancellable Promise with extra features
CPromise.CanceledError : CanceledError
CanceledError class
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.AbortController : AbortController | AbortControllerEx
Refers to the AbortController class (native if available)
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.AbortControllerEx : AbortControllerEx
AbortControllerEx class
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.E_REASON_CANCELED
Generic cancellation reason
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.E_REASON_DISPOSED
Cancellation reason for the case when the instance will be disposed
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.E_REASON_TIMEOUT
Timeout cancellation reason
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.async : function
async decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.listen : function
listen decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.cancel : function
cancel decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.timeout : function
timeout decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.innerWeight : function
innerWeight decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.label : function
label decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.canceled : function
label decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.progress : function
progress decorator
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise.promisify : function
Kind: static property of CPromise
CPromise~CPromise ⇐ Promise
CPromise class
Kind: inner class of CPromise
Extends: Promise
- ~CPromise ⇐
Promise- new CPromise([executor], [options])
- instance
- .signal :
AbortSignal - .isPending ⇒
Boolean - .isCanceled ⇒
Boolean - .isCaptured ⇒
Boolean - .isPaused ⇒
Boolean - .isRejected ⇒
Boolean - .parent ⇒
CPromise|null - .onCancel(listener) ⇒
CPromise - .onPause(listener) ⇒
CPromise - .onResume(listener) ⇒
CPromise - .onCapture(listener) ⇒
CPromise - .totalWeight([weight]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .innerWeight([weight]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .progress([value], [data], [scope]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .propagate(type, data, [scope]) ⇒
CPromise - .captureProgress([options]) ⇒
CPromise - .scopes([pendingOnly]) ⇒
Array.<CPromise> - .timeout([ms]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .weight([weight]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .label([label]) ⇒
Number|CPromise - .resolve(value) ⇒
CPromise - .reject(err) ⇒
CPromise - .pause() ⇒
Boolean - .resume() ⇒
Boolean - .atomic([type]) ⇒
- .cancel([reason], [force])
- .emitSignal(type, [data], [handler], [locator]) ⇒
Boolean - .delay(ms) ⇒
CPromise - .then(onFulfilled, [onRejected]) ⇒
CPromise - .catch(onRejected, [filter]) ⇒
CPromise - .canceled([onCanceled]) ⇒
CPromise - .listen(signal) ⇒
CPromise - .on(type, listener, [prepend]) ⇒
CPromise - .off(type, listener) ⇒
CPromise - .listenersCount(type) ⇒
Number - .hasListeners(type) ⇒
Boolean - .once(type, listener) ⇒
CPromise - .emit(type, ...args) ⇒
CPromise - .emitHook(type, ...args) ⇒
Boolean - .toString([entireChain]) ⇒
string
- .signal :
- static
- .isCanceledError(thing) ⇒
boolean - .delay(ms, value) ⇒
CPromise - .all(iterable, [options]) ⇒
CPromise - .race(thenables) ⇒
CPromise - .allSettled(iterable, options) ⇒
CPromise - .retry(fn, [options]) ⇒
CPromise - .from(thing, [options]) ⇒
CPromise - .promisify(originalFn, [options]) ⇒
function - .run(generatorFn, [options]) ⇒
CPromise
- .isCanceledError(thing) ⇒
new CPromise([executor], [options])
Creates a new CPromise instance
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [executor] | CPromiseExecutorFn |
promise executor function that will be invoked in the context of the new CPromise instance |
| [options] | CPromiseOptions |
cPromise.signal : AbortSignal
get promise abort signal object
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.isPending ⇒ Boolean
indicates if the promise is pending
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.isCanceled ⇒ Boolean
indicates if the promise is pending
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.isCaptured ⇒ Boolean
indicates if the promise progress is captured
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.isPaused ⇒ Boolean
indicates if the promise is paused
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.isRejected ⇒ Boolean
indicates if the promise is rejected
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.parent ⇒ CPromise | null
get parent promise
Kind: instance property of CPromise
cPromise.onCancel(listener) ⇒ CPromise
registers the listener for cancel event
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| listener | OnCancelListener |
cPromise.onPause(listener) ⇒ CPromise
registers the listener for pause event
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| listener | OnPauseListener |
cPromise.onResume(listener) ⇒ CPromise
registers the listener for resume event
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| listener | OnResumeListener |
cPromise.onCapture(listener) ⇒ CPromise
registers the listener for capture event
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| listener | OnCaptureListener |
cPromise.totalWeight([weight]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
Set or get the total weight of the inner chains
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [weight] | Number |
cPromise.innerWeight([weight]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
Set or get the total weight of the inner chains
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [weight] | Number |
cPromise.progress([value], [data], [scope]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
Set promise progress
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [value] | Number |
a number between [0, 1] |
| [data] | * |
any data to send for progress event listeners |
| [scope] | CPromise |
CPromise scope |
cPromise.propagate(type, data, [scope]) ⇒ CPromise
emit propagate event that will propagate through each promise scope in the chain (bubbling)
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | symbol |
some type to identify the data kind | |
| data | * |
|
some data |
| [scope] | CPromise |
|
CPromise scope |
cPromise.captureProgress([options]) ⇒ CPromise
capture initial progress state of the chain
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [options] | Object |
|
| options.throttle | Number |
set min interval for firing progress event |
| options.innerWeight | Number |
set weight of the nested promises |
cPromise.scopes([pendingOnly]) ⇒ Array.<CPromise>
Returns all parent scopes that are in pending state
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| [pendingOnly] | boolean |
false |
cPromise.timeout([ms]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
timeout before the promise will be canceled
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [ms] | Number |
timeout in ms |
cPromise.weight([weight]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
Sets the promise weight in progress capturing process
Kind: instance method of CPromise
Returns: Number | CPromise - returns weight if no arguments were specified
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [weight] | Number |
any number greater or equal 0 |
cPromise.label([label]) ⇒ Number | CPromise
Sets the promise label
Kind: instance method of CPromise
Returns: Number | CPromise - returns weight if no arguments were specified
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [label] | String |
any string |
cPromise.resolve(value) ⇒ CPromise
Resolves the promise with given value
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param |
|---|
| value |
cPromise.reject(err) ⇒ CPromise
Rejects the promise with given error
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param |
|---|
| err |
cPromise.pause() ⇒ Boolean
Pause promise
Kind: instance method of CPromise
cPromise.resume() ⇒ Boolean
Resume promise
Kind: instance method of CPromise
cPromise.atomic([type]) ⇒
Make promise chain atomic (non-cancellable for external signals)
Kind: instance method of CPromise
Returns: CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [type] | number | boolean | "disabled" | "detached" | "await" |
cPromise.cancel([reason], [force])
throws the CanceledError that cause promise chain cancellation
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| [reason] | String | Error |
|
| [force] | Boolean |
false |
cPromise.emitSignal(type, [data], [handler], [locator]) ⇒ Boolean
Emit a signal of the specific type
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | Signal |
| [data] | * |
| [handler] | SignalHandler |
| [locator] | SignalLocator |
cPromise.delay(ms) ⇒ CPromise
Returns a chain that will be resolved after specified timeout
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| ms | Number |
cPromise.then(onFulfilled, [onRejected]) ⇒ CPromise
returns a CPromise. It takes up to two arguments: callback functions for the success and failure cases of the Promise.
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| onFulfilled | onFulfilled |
| [onRejected] | onRejected |
cPromise.catch(onRejected, [filter]) ⇒ CPromise
Catches rejection with optionally specified Error class
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| onRejected | function |
| [filter] | Error |
cPromise.canceled([onCanceled]) ⇒ CPromise
Catches CancelError rejection
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| [onCanceled] | function |
cPromise.listen(signal) ⇒ CPromise
Listen for abort signal
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| signal | AbortSignal |
cPromise.on(type, listener, [prepend]) ⇒ CPromise
adds a new listener
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| type | EventType |
|
| listener | function |
|
| [prepend] | Boolean |
false |
cPromise.off(type, listener) ⇒ CPromise
removes the listener
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | EventType |
| listener | function |
cPromise.listenersCount(type) ⇒ Number
returns listeners count of the specific event type
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | EventType |
cPromise.hasListeners(type) ⇒ Boolean
checks if there are listeners of a specific type
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | String | Symbol |
cPromise.once(type, listener) ⇒ CPromise
add 'once' listener
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | EventType |
| listener | function |
cPromise.emit(type, ...args) ⇒ CPromise
emits the event
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | EventType |
| ...args |
cPromise.emitHook(type, ...args) ⇒ Boolean
Emits event as a hook. If some listener return true, this method will immediately return true as the result. Else false will be retuned
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| type | EventType |
| ...args |
cPromise.toString([entireChain]) ⇒ string
Render promise to String
Kind: instance method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| [entireChain] | boolean |
false |
render the entire promise chain |
CPromise.isCanceledError(thing) ⇒ boolean
Checks if thing is an CanceledError instance
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param |
|---|
| thing |
CPromise.delay(ms, value) ⇒ CPromise
Returns a CPromise that will be resolved after specified timeout
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ms | Number |
delay before resolve the promise with specified value |
| value |
CPromise.all(iterable, [options]) ⇒ CPromise
Returns a single CPromise that resolves to an array of the results of the input promises. If one fails then other promises will be canceled immediately
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| iterable | Iterable | Generator | GeneratorFunction |
| [options] | AllOptions |
Example
CPromise.all(function*(){
yield axios.get(url1);
yield axios.get(url2);
yield axios.get(url3);
}, {concurrency: 1}).then(console.log)CPromise.race(thenables) ⇒ CPromise
returns a promise that fulfills or rejects as soon as one of the promises in an iterable fulfills or rejects, with the value or reason from that promise. Other pending promises will be canceled immediately
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| thenables | Iterable |
CPromise.allSettled(iterable, options) ⇒ CPromise
returns a promise that resolves after all of the given promises have either fulfilled or rejected
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| iterable | Iterable | Generator | GeneratorFunction |
| options | AllOptions |
CPromise.retry(fn, [options]) ⇒ CPromise
Retry async operation
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| fn | CPGeneratorRetryFunction | CPRetryFunction |
| [options] | object |
| [options.args] | array |
| [options.retries] | number |
| [options.delayWeight] | number | CPRetryDelayResolver |
| [options.delay] | object |
CPromise.from(thing, [options]) ⇒ CPromise
Converts thing to CPromise using the following rules:
- CPromise instance returns as is
- Objects with special method defined with key
Symbol.for('toCPromise')will be converted using this method The result will be cached for future calls - Thenable wraps into a new CPromise instance, if thenable has the
cancelmethod it will be used for canceling - Generator function will be resolved to CPromise
- Array will be resoled via
CPromise.all, arrays with one element (e.g.[[1000]]) will be resolved viaCPromise.race
This method returns null if the conversion failed.
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|
| thing | * |
|
| [options] | Object |
|
| [options.resolveSignatures] | Boolean |
true |
| [options.args] | Array |
CPromise.promisify(originalFn, [options]) ⇒ function
Converts callback styled function|GeneratorFn|AsyncFn to CPromise async function
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| originalFn | function | GeneratorFunction | AsyncFunction |
| [options] | PromisifyOptions | function | Boolean |
CPromise.run(generatorFn, [options]) ⇒ CPromise
Resolves the generator to an CPromise instance
Kind: static method of CPromise
| Param | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| generatorFn | GeneratorFunction |
|
| [options] | Object |
|
| [options.args] | Array |
|
| [options.resolveSignatures] | Boolean |
resolve extra signatures (like arrays with CPromise.all) |
| [options.scopeArg] | Boolean |
pass the CPromise scope as the first argument to the generator function |
| [options.context] | * |
CPromise~EventType : String | Symbol
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
CPromise~CPromiseExecutorFn : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
this: CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| resolve | function |
| reject | function |
| scope | CPromise |
CPromise~PromiseOptionsObject : Object
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
Properties
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| label | String |
||
| timeout | Number |
||
| weight | Number |
||
| [nativeController] | Boolean |
false |
prefer native AbortController class as the internal signal |
CPromise~CPromiseOptions : PromiseOptionsObject | String | Number
If value is a number it will be considered as the value for timeout option If value is a string it will be considered as a label
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
CPromise~OnCancelListener : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| reason | CanceledError |
CPromise~OnPauseListener : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
CPromise~OnResumeListener : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
CPromise~OnCaptureListener : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| CPromise | scope |
CPromise~Signal : String | Symbol
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
CPromise~SignalHandler ⇒ Boolean
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
this: {CPromise}
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| data | * |
| type | Signal |
| scope | CPromise |
CPromise~SignalLocator ⇒ Boolean
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
this: {CPromise}
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| data | * |
| type | Signal |
| scope | CPromise |
| isRoot | Boolean |
CPromise~AllOptions : object
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| concurrency | number |
limit concurrency of promise being run simultaneously |
| mapper | function |
function to map each element |
| ignoreResults | boolean |
do not collect results |
| signatures | boolean |
use advanced signatures for vales resolving |
CPromise~CPRetryFunction ⇒ *
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| attempt | number |
| args | array |
CPromise~CPGeneratorRetryFunction ⇒ *
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| scope | CPromise |
| attempt | number |
| args | array |
CPromise~CPRetryDelayResolver ⇒ number
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
Returns: number - a delay in ms before next attempt
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| attempt | number |
| retries | number |
CPromise~PromisifyFinalizeFn : function
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
| Param | Type |
|---|---|
| result | * |
| scope | CPromise |
CPromise~PromisifyOptions : Object
Kind: inner typedef of CPromise
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| [multiArgs] | Boolean |
aggregate all passed arguments to an array |
| [finalize] | PromisifyFinalizeFn |
aggregate all passed arguments to an array |
| [fnType] | "plain" | "generator" | "async" |
|
| [scopeArg] | boolean |
pass the CPromise scope as the first argument to the generator function |
License
The MIT License Copyright (c) 2020 Dmitriy Mozgovoy robotshara@gmail.com
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.


