Package Exports
- datastructures-js
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (datastructures-js) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme

Javascript implementation of the main data structures. Each data structure object is constructed using a factory function that holds the data structure name.
Install
npm install datastructures-jsUsage
let ds = require('datastructures-js');Data Structures
- Stack
- Queue
- Priority Queue
- Set
- Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Binary Search Tree
- Graph
- Directed Graph
Contribution & License
Stack
elements data type: any type.
construction
let stack = ds.stack();.push(element)
push an element to the top of the stack.
stack.push('test');.peek()
returns the top element in the stack.
let element = stack.peek(); // test.pop()
pops the top element of the stack.
let element = stack.pop(); // test.isEmpty()
checks if the stack is empty.
let isEmpty = stack.isEmpty(); // true.length()
returns the length length of the stack.
let length = stack.length(); // 0Queue
elements data type: any type.
construction
let queue = ds.queue();
// OR
let queue = ds.q();.enqueue(element)
adds an element to the back of the queue.
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(20);.front()
returns the front element in queue.
let front = queue.front(); // 10.back()
returns the back element in the queue.
let back = queue.back(); // 20.dequeue()
dequeues an element from the queue.
let element = queue.dequeue(); // 10.isEmpty()
checks if the queue is empty.
let isEmpty = queue.isEmpty(); // false.length()
returns the length of the queue
var length = queue.length(); // 1.toArray()
converts the queue to an array with front starting at 0
queue.enqueue(1);
queue.enqueue(4);
queue.enqueue(2);
let elements = queue.toArray(); // [1, 4, 2].clear()
clears the queue
queue.clear();
queue.length(); // 0PriorityQueue
elements data type: any type.
construction
let pQueue = ds.priorityQueue();
// OR
let pQueue = ds.pq();.enqueue(element, priority)
adds an element with priority (number) to the back of the queue.
pQueue.enqueue('patient 1', 2); // lower priority
pQueue.enqueue('patient 2', 1); // higher priority.front()
returns the front element in queue.
var front = pQueue.front(); // patient 1.back()
returns the back element in the queue.
var back = pQueue.back(); // patient 3.dequeue()
dequeues the highest priority element from the queue.
var element = pQueue.dequeue(); // patient 2.isEmpty()
checks if the queue is empty.
var isEmpty = queue.isEmpty(); // false.length()
returns the length of the queue.
var len = queue.length(); // 1converts the queue to an array in the order elements were queued
queue.enqueue('test 1', 2);
queue.enqueue('test 2', 3);
queue.enqueue('test 3', 1);
let elements = queue.toArray(); // ['test 1', 'test 2', 'test 3'].clear()
clears the queue
queue.clear();
queue.length(); // 0Set
elements data type: number, string, boolean, null, undefined.
construction
let set = ds.set();.add(element)
adds an element to the set.
set.add('A');
set.add('B');
set.add('C');
set.add('D');.isEmpty()
checks if the set is empty.
let isEmpty = set.isEmpty(); // false.contains(element)
checks if the set contains an element
let contains = set.contains('C'); // true.remove(element)
removes an element from the set.
set.remove('C');
console.log(set.contains('C')); // false.size()
returns the number of elements in the set.
let size = set.size(); // 3.union(set)
unions the set with another set and returns the resulting set.
let set2 = ds.set();
set2.add('A');
set2.add('E');
set2.add('F');
let unionSet = set.union(set2); // unionSet contains A, B, D, E, F.intersect(set)
intersects the set with another set and returns the resulting set.
let set2 = ds.set();
set2.add('A');
set2.add('E');
set2.add('F');
// set contains A, B, D
let intersectSet = set.intersect(set2); // intersectSet contains A.diff(set)
returns the diff set between the set and another set.
let set2 = ds.set();
set2.add('A');
set2.add('E');
set2.add('F');
// set contains A, B, D
let diffSet = set.diff(set2); // diffSet contains B, D.isSubset(set)
checks if the set is a subset of another set
let s1 = ds.set();
s1.add('B');
s1.add('G');
s1.add('D');
let s2 = ds.set();
s2.add('A');
s2.add('G');
s2.add('B');
s2.add('G');
s2.add('D');
let d1 = s2.isSubset(s1); // false
let d2 = s1.isSubset(s2); // true.toArray()
converts the set into an array.
let arr = set.toArray(); // ['A', 'B', 'D'].clear()
clears the set
set.clear(); // set is emptyLinkedList
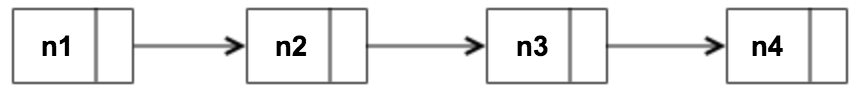
node value data type: number, string, boolean, null, undefined.
construction
let linkedList = ds.linkedList();
// OR
let linkedList = ds.ll();.addFirst(value)
add a node with the specified value to the beginning of the list.
linkedList.addFirst('n1');.addLast(value)
add a node with the specified value to the end of the list.
linkedList.addLast('n4');.addAfter(value, newValue)
add a node with newValue after an existing value's node, throws exception if value doesnt exist.
try {
linkedList.addAfter('n1', 'n2');
linkedList.addAfter('n33', 'n3');
}
catch (e) {
console.log(e.message); // node n33 not found
}.addBefore(value, newValue)
add a node with newValue before an existing value's node, throws exception if value doesnt exist.
try {
linkedList.addBefore('n4', 'n3');
linkedList.addBefore('n33', 'n3');
}
catch (e) {
console.log(e.message); // node n33 not found
}.find(value)
returns a linkedListNode object that contains two functions:
- .getNext() returns the next linkedListNode object.
- .getValue() returns the node value.
let n3 = linkedList.find('n3');
console.log(n3.getValue()); // n3
console.log(n3.getNext().getValue()); // n4.head()
returns the first linkedListNode object in the list.
let head = linkedList.head();
console.log(head.getValue()); // n1.traverse(cb)
traverse the linked list and calls cb for each node
linkedList.traverse((value) => {
console.log(value);
});
// n1
// n2
// n3
// n4.remove(value)
remove the value's node from the list or throw an exception if value not found.
linkedList.remove('n3');.removeFirst()
removes the first node in the list.
linkedList.removeFirst(); // n1 removed.removeLast()
removes the last node in the list.
linkedList.removeLast(); // n4 removed.length()
returns the number of nodes in the list.
let length = linkedList.count(); // 1.clear()
removes all the nodes from the list.
linkedList.clear();
console.log(linkedList.length()); // 0 DoublyLinkedList

node value data type: number, string, boolean, null, undefined.
construction
let dList = ds.doublyLinkedList();
// OR
let dList = ds.dll();.addFirst(value)
add a node with the specified value to the beginning of the list.
dList.addFirst('n1');.addLast(value)
add a node with the specified value to the end of the list.
dList.addLast('n4');.addAfter(value, newValue)
add a node with newValue after an existing value's node, throws exception if value doesnt exist.
try {
dList.addAfter('n1', 'n2');
dList.addAfter('n33', 'n2');
}
catch (e) {
console.log(e.message); // node n33 not found
}.addBefore(value, newValue)
add a node with newValue before an existing value's node, throws exception if value doesnt exist.
try {
dList.addBefore('n4', 'n3');
dList.addBefore('n33', 'n2');
}
catch (e) {
console.log(e.message); // node n33 not found
}.find(value)
returns a doublyLinkedListNode object that contains three functions:
- .getNext() returns the next doublyLinkedListNode object.
- .getPrev() returns the previous doublyLinkedListNode object.
- .getValue() returns the node's value.
let n3 = dList.find('n3');
console.log(n3.getValue()); // n3
console.log(n3.getNext().getValue()); // n4
console.log(n3.getPrev().getValue()); // n2.head()
returns the first doublyLinkedListNode object in the list.
let head = dList.head();
console.log(head.getValue()); // n1.tail()
returns the last doublyLinkedListNode object in the list.
let tail = dList.tail();
console.log(tail.getValue()); // n4.removeFirst()
removes the first node from the list.
dList.removeFirst();.removeLast()
removes the last node from the list.
dList.removeLast();.remove(value)
remove the value's node from the list.
dList.remove('n2');.length()
returns the number of nodes in the list.
let length = dList.length();.clear()
clears all the nodes from the list.
dList.clear();BinarySearchTree

node value data type: string, number
construction
let bst = ds.binarySearchTree();
// OR
let bst = ds.bst();.insert(value)
inserts a node with the specified value into the tree.
bst.insert(50);
bst.insert(80);
bst.insert(30);
bst.insert(90);
bst.insert(60);
bst.insert(40);
bst.insert(20);.root()
returns the root node
let root = bst.root().getValue(); // 90.min()
returns the min value binaryNode object (most left node value).
let min = bst.min().getValue(); // 20.max()
returns the max value binaryNode object (most right node value).
let max = bst.max().getValue(); // 90.count()
returns number of nodes in the tree
let count = bst.count(); // 7.find(value)
returns a binaryNode object that contains three functions:
- .getRight() returns the right child binaryNode node object.
- .getLeft() returns the left child binaryNode node object.
- .getValue() returns the node value.
let n = bst.find(30);
console.log(n.getValue()); // 30
console.log(n.getRight().getValue()); // 40
console.log(n.getLeft().getValue()); // 20.traverse(cb, order)
traverse the tree in the defined order and apply a callback on each node.
- order: 'inOrder' OR 'preOrder' OR 'postOrder'. default is 'inOrder'
// inOrder traverse
bst.traverse((value) => {
console.log(value);
});
// 20
// 30
// 40
// 50
// 60
// 80
// 90
// preOrder traverse
bst.traverse((value) => console.log(value), 'preOrder');
// 50
// 30
// 20
// 40
// 80
// 60
// 90
// postOrder traverse
bst.traverse((value) => console.log(value), 'postOrder');
// 20
// 40
// 30
// 60
// 90
// 80
// 50.remove(value)
removes a value's node (if exists) from the tree.
bst.remove(30);
let n50 = bst.find(50);
let n40 = bst.find(40);
console.log(n50.getLeft().getValue()); // 40
console.log(n40.getLeft().getValue()); // 20.clear()
clears all the nodes from the tree.
bst.clear();Graph

vertex data type: string, number, boolean, null, undefined
construction
let graph = ds.graph();
// OR
let graph = ds.g();.addVertex(vertex)
adds a vertex to the graph.
graph.addVertex('test');.hasVertex(vertex)
checks if the graph has a vertex
let check = graph.hasVertex('test'); // true.removeVertex(vertex)
checks if the graph has a vertex
graph.removeVertex('test');
graph.hasVertex('test'); // false.addEdge(v1, v2, weight)
adds a weighted edge between two existing vertices.
graph.addVertex('v1');
graph.addVertex('v2');
graph.addEdge('v1', 'v2', 3).hasEdge(v1, v2)
checks if the graph has an edge between two exsiting vertices
let check = graph.hasEdge('v1', 'v2'); // true.getWeight(v1, v2)
returns the weight between two vertices
let w = graph.getWeight('v1', 'v2'); // 3.removeEdge(v1, v2)
removes an existing edge in the graph
graph.removeEdge('v1', 'v2');
graph.hasEdge('v1', 'v2'); // false
graph.hasEdge('v2', 'v1'); // false.addPath(v1, v2, weight)
adds an edge between two vertices and creates the vertices if one or both dont exist.
// building the diagram graph
graph.addPath('v1', 'v2', 2);
graph.addPath('v2', 'v3', 3);
graph.addPath('v1', 'v3', 6);
graph.addPath('v2', 'v4', 1);
graph.addPath('v4', 'v3', 1);
graph.addPath('v4', 'v5', 4);
graph.addPath('v3', 'v5', 2);.countVertices()
returns the number of vertices in the graph.
let count = graph.countVertices(); // 5.traverse(vertex, cb, type)
traverse the graph.
- type: 'bfs' OR 'dfs' (breadth-first search or depth-first search). default is 'bfs'
// bfs traverse
graph.traverse('v5', (v) => console.log(v), 'bfs');
// v5
// v4
// v3
// v2
// v1
// dfs traverse
graph.traverse('v1', (v) => console.log(v), 'dfs');
// v1
// v2
// v3
// v4
// v5.findShortestPath(v1, v2)
find all possible shortests paths between two vertices in the graph
let shortestPath = graph.findShortestPath('v1', 'v5'); // [ ['v1', 'v2', 'v4', 'v3', 'v5'] ].clear()
clears all the nodes from the graph.
graph.clear();DirectedGraph

construction
let dgraph = ds.directedGraph();
// OR
let dgraph = ds.dg();.addVertex(vertex)
adds a vertex to the graph.
dgraph.addVertex('test');.hasVertex(vertex)
checks if the graph has a vertex
let check = dgraph.hasVertex('test'); // true.removeVertex(vertex)
checks if the graph has a vertex
dgraph.removeVertex('test');
dgraph.hasVertex('test'); // false.addEdge(v1, v2, weight)
adds a weighted direction from v1 to v2
dgraph.addVertex('v1');
dgraph.addVertex('v2');
dgraph.addEdge('v1', 'v2', 3);.hasEdge(v1, v2)
checks if the graph has a direction from v1 to v2
let check1 = dgraph.hasEdge('v1', 'v2'); // true
let check2 = dgraph.hasEdge('v2', 'v1'); // false.getWeight(v1, v2)
returns the weight from v1 to v2
let w = dgraph.getWeight('v1', 'v2'); // 3.removeEdge(v1, v2)
removes the direction from v1 to v2
dgraph.removeEdge('v1', 'v2');
dgraph.hasEdge('v1', 'v2'); // false.addPath(v1, v2, weight)
adds a direction from v1 to v2 and creates both vertices if not exist
// build the diagram dgraph
dgraph.addPath('v1', 'v2', 2);
dgraph.addPath('v1', 'v3', 3);
dgraph.addPath('v1', 'v4', 1);
dgraph.addPath('v2', 'v4', 1);
dgraph.addPath('v3', 'v5', 2);
dgraph.addPath('v4', 'v3', 1);
dgraph.addPath('v4', 'v5', 4);.countVertices()
returns the number of vertices in the graph.
let count = dgraph.countVertices(); // 5.traverse(vertex, cb, type)
traverse the graph.
- type: 'bfs' OR 'dfs' (breadth-first search or depth-first search). default is 'bfs'
// bfs traverse
dgraph.traverse('v1', (v) => console.log(v), 'bfs');
// v1
// v2
// v3
// v4
// v5
// dfs traverse
dgraph.traverse('v5', (v) => console.log(v), 'dfs');
// v1
// v2
// v4
// v3
// v5.findShortestPath(v1, v2)
find all possible shortests paths between two vertices in the graph
let shortestPath = dgraph.findShortestPath('v1', 'v5'); // [ ['v1', 'v4', 'v3', 'v5'] ].clear()
clears all the nodes from the graph.
dgraph.clear();Contribution
Fork and then clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/[your-username]/datastructures-jsInstall grunt-cli
npm install -g grunt-cliinstall dependencies
npm installCreate a branch from development branch with a name indicatig the fix/feature
git checkout -b fix-branchrun all tasks
grunt buildto run lint only
grunt lintto run tests only
grunt testto run test coverage only
grunt coveragewhen everything is OK, push the changes to the same branch
git push origin fix-branchand create a pull request from development branch.
Changes are reviewed and merged if all is ok.
Thanks.
License
The MIT License. Full License is here


