Package Exports
- react-tracked
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (react-tracked) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme

react-tracked
Super fast React global/shared state with context and hooks
Documentation site: https://react-tracked.js.org
If you are looking for a Redux-based library, please visit reactive-react-redux which has the same hooks API.
Introduction
React Context and useContext is often used to avoid prop drilling, however it's known that there's a performance issue. When a context value is changed, all components that useContext will re-render. React idiomatic usage of the Context API is to separate concerns into pieces and use multiple contexts. If each context value is small enough, there shouldn't be any performance issue.
What if one wants to put a bigger state object into a context for various reasons? React Redux is one solution in this field. Redux is designed to handle one big global state, and React Redux optimizes that use case.
This library tosses a new option. It's based on Context and
typically with useReducer, and provides APIs to solve
the performance issue.
Most notably, it comes with useTrackedState, which allows
optimization without hassle. Technically, it uses Proxy underneath,
and it tracks state usage in render so that if only used part of the state
is changed, it will re-render.
Install
npm install react-trackedUsage (useTracked)
The following shows a minimal example. Please check out others in the examples folder.
import React, { useReducer } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { createContainer } from 'react-tracked';
const useValue = ({ reducer, initialState }) => useReducer(reducer, initialState);
const { Provider, useTracked } = createContainer(useValue);
const initialState = {
count: 0,
text: 'hello',
};
const reducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'increment': return { ...state, count: state.count + 1 };
case 'decrement': return { ...state, count: state.count - 1 };
case 'setText': return { ...state, text: action.text };
default: throw new Error(`unknown action type: ${action.type}`);
}
};
const Counter = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useTracked();
return (
<div>
{Math.random()}
<div>
<span>Count: {state.count}</span>
<button type="button" onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'increment' })}>+1</button>
<button type="button" onClick={() => dispatch({ type: 'decrement' })}>-1</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
const TextBox = () => {
const [state, dispatch] = useTracked();
return (
<div>
{Math.random()}
<div>
<span>Text: {state.text}</span>
<input value={state.text} onChange={event => dispatch({ type: 'setText', text: event.target.value })} />
</div>
</div>
);
};
const App = () => (
<Provider reducer={reducer} initialState={initialState}>
<h1>Counter</h1>
<Counter />
<Counter />
<h1>TextBox</h1>
<TextBox />
<TextBox />
</Provider>
);
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'));Technical memo
React context by nature triggers propagation of component re-rendering
if a value is changed. To avoid this, this libraries use undocumented
feature of calculateChangedBits. It then uses a subscription model
to force update when a component needs to re-render.
API
Recipes
Caveats
Examples
The examples folder contains working examples. You can run one of them with
PORT=8080 npm run examples:minimaland open http://localhost:8080 in your web browser.
You can also try them in codesandbox.io: 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10
Related projects
| Context value | Using subscriptions | Optimization for rendering big object | Dependencies | Package size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| react-tracked | state-based object | Yes *1 | Proxy-based tracking | No | 1.5kB |
| constate | state-based object | No | No (should use multiple contexts) | No | 329B |
| unstated-next | state-based object | No | No (should use multiple contexts) | No | 362B |
| zustand | N/A | Yes | Selector function | No | 742B |
| react-sweet-state | state-based object | Yes *3 | Selector function | No | 4.5kB |
| storeon | store | Yes | state names | No | 337B |
| react-hooks-global-state | state object | No *2 | state names | No | 913B |
| react-redux (hooks) | store | Yes | Selector function | Redux | 5.6kB |
| reactive-react-redux | state-based object | Yes *1 | Proxy-based tracking | Redux | 1.4kB |
| easy-peasy | store | Yes | Selector function | Redux, immer, and so on | 9.5kB |
| mobx-react-lite | mutable state object | No *4 | Proxy-based tracking | MobX | 1.7kB |
| hookstate | N/A | Yes | Proxy-based tracking | No | 2.6kB |
- *1 Stops context propagation by
calculateChangedBits=0 - *2 Uses
observedBits - *3 Hack with readContext
- *4 Mutation trapped by Proxy triggers re-render
Benchmarks
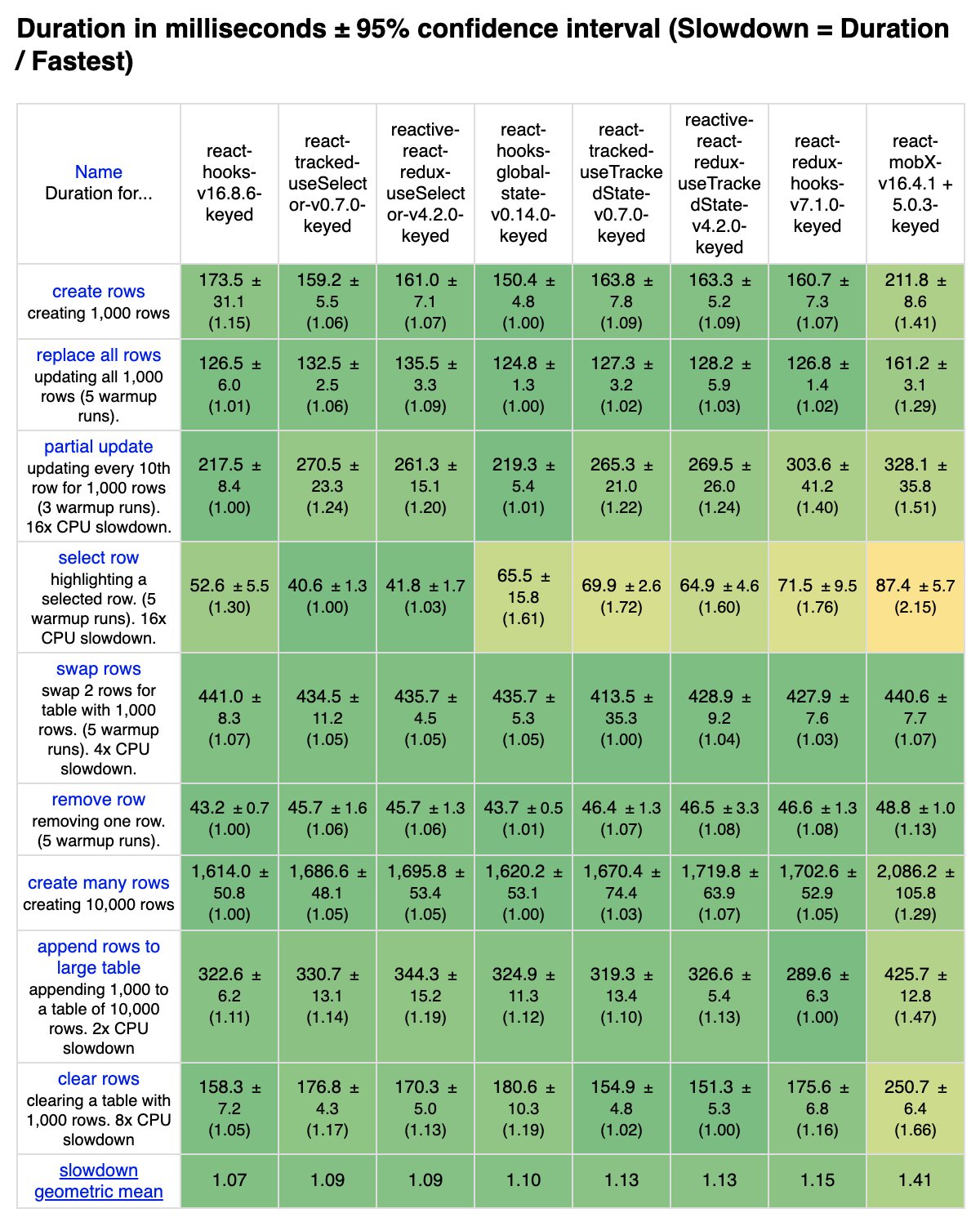
See this for details.
Blogs
- Super performant global state with React context and hooks
- Redux-less context-based useSelector hook that has same performance as React-Redux
- Four different approaches to non-Redux global state libraries
- What is state usage tracking? A novel approach to intuitive and performant global state with React hooks and Proxy
- How to use react-tracked: React hooks-oriented Todo List example
- Effortless render optimization with state usage tracking with React hooks
- 4 options to prevent extra rerenders with React context