Package Exports
- typescript-json
- typescript-json/lib/factories/CommentFactory
- typescript-json/lib/factories/CommentFactory.js
- typescript-json/lib/factories/ExpressionFactory
- typescript-json/lib/factories/ExpressionFactory.js
- typescript-json/lib/factories/MetadataCollection
- typescript-json/lib/factories/MetadataCollection.js
- typescript-json/lib/factories/MetadataFactory
- typescript-json/lib/factories/MetadataFactory.js
- typescript-json/lib/factories/TypeFactory
- typescript-json/lib/factories/TypeFactory.js
- typescript-json/lib/index.js
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/ApplicationProgrammer
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/ApplicationProgrammer.js
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/AssertProgrammer
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/AssertProgrammer.js
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/StringifyProgrammer
- typescript-json/lib/programmers/StringifyProgrammer.js
- typescript-json/lib/utils/Escaper
- typescript-json/lib/utils/Escaper.js
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (typescript-json) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
Deprecated
typescript-jsonhas been renamed totypia
Typia
// RUNTIME VALIDATORS
export function is<T>(input: unknown | T): input is T; // returns boolean
export function assert<T>(input: unknown | T): T; // throws TypeGuardError
export function validate<T>(input: unknown | T): IValidation<T>; // detailed
// STRICT VALIDATORS
export function equals<T>(input: unknown | T): input is T;
export function assertEquals<T>(input: unknown | T): T;
export function validateEquals<T>(input: unknown | T): IValidation<T>;
// JSON
export function application<T>(): IJsonApplication; // JSON schema
export function assertParse<T>(input: string): T; // type safe parser
export function assertStringify<T>(input: T): string; // safe and faster
// +) isParse, validateParse
// +) stringify, isStringify, validateStringify
// MISC
export function random<T>(): Primitive<T>; // generate random data
export function clone<T>(input: T): Primitive<T>; // deep clone
export function prune<T extends object>(input: T): void; // erase extra props
// +) isClone, assertClone, validateClone
// +) isPrune, assertPrune, validatePrunetypia is a transformer library of TypeScript, supporting below features:
- Super-fast Runtime Validators
- Safe JSON parse and fast stringify functions
- JSON schema generator
- Random data generator
All functions in typia require only one line. You don't need any extra dedication like JSON schema definitions or decorator function calls. Just call typia function with only one line like typia.assert<T>(input).
Also, as typia performs AOT (Ahead of Time) compilation skill, its performance is much faster than other competitive libaries. For an example, when comparing validate function is() with other competitive libraries, typia is maximum 15,000x times faster than class-validator.
Measured on Intel i5-1135g7, Surface Pro 8
Sponsors and Backers
Thanks for your support.
Your donation would encourage typia development.
Setup
Setup Wizard
npx typia setupJust type npx typia setup, that's all.
If you've installed ttypescript during setup, you should compile typia utilization code through ttsc command, instead of tsc.
# COMPILE THROUGH TTYPESCRIPT
npx ttsc
# RUN TS-NODE WITH TTYPESCRIPT
npx ts-node -C ttypescript src/index.tsOtherwise, you've chosen ts-patch, you can use original tsc command. However, ts-patch hacks node_modules/typescript source code. Also, whenever update typescript version, you've to run npm run prepare command repeatedly.
By the way, when using @nest/cli, you must just choose ts-patch
# USE ORIGINAL TSC COMMAND
tsc
npx ts-node src/index.ts
# WHENVER UPDATE
npm install --save-dev typescript@latest
npm run prepareManual Setup
If you want to install and setup typia manually, read Guide Documents - Setup.
Vite
When you want to setup typia on your frontend project with vite, just configure vite.config.ts like below.
Also, don't forget running Setup Wizard before.
If you've chosen ts-patch compiler, just call only typescript() function.
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react";
import typescript from "@rollup/plugin-typescript";
import ttsc from "ttypescript";
// https://vitejs.dev/config/
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
react(),
// when using "ttypescript"
typescript({
typescript: ttsc,
}),
// otherwise using "ts-patch"
typescript()
]
});Features
In here README documents, only summarized informations are provided.
For more details, refer to the Guide Documents (wiki).
- Runtime Validators
- Enhanced JSON
- Miscellaneous
Runtime Validators
// ALLOW SUPERFLUOUS PROPERTIES
export function is<T>(input: T | unknown): input is T; // returns boolean
export function assert<T>(input: T | unknown): T; // throws `TypeGuardError`
export function validate<T>(input: T | unknown): IValidation<T>; // detailed
// DO NOT ALLOW SUPERFLUOUS PROPERTIES
export function equals<T>(input: T | unknown): input is T;
export function assertEquals<T>(input: T | unknown): T;
export function validateEquals<T>(input: T | unknown): IValidation<T>;
// REUSABLE FACTORY FUNCTIONS
export function createIs<T>(): (input: unknown) => input is T;
export function createAssert<T>(): (input: unknown) => T;
export function createValidate<T>(): (input: unknown) => IValidation<T>;
export function createEquals<T>(): (input: unknown) => input is T;
export function createAssertEquals<T>(): (input: unknown) => T;
export function createValidateEquals<T>(): (input: unknown) => IValidation<T>;typia supports three type of validator functions:
is(): returnsfalseif not matched with the typeTassert(): throws aTypeGuardErrorwhen not matchedvalidate()- when matched, returns
IValidation.ISuccess<T>withvalueproperty - when not matched, returns
IValidation.IFailurewitherrorsproperty
- when matched, returns
Also, if you want more strict validator functions that even do not allowing superfluous properties not written in the type T, you can use those functions instead; equals(), assertEquals(), validateEquals(). Otherwise you want to create resuable validator functions, you can utilize factory functions like createIs() instead.
When you want to add special validation logics, like limiting range of numeric values, you can do it through comment tags. If you want to know about it, visit the Guide Documents (Features > Runtime Validators > Comment Tags).
Enhanced JSON
// JSON SCHEMA GENERATOR
export function application<
Types extends unknown[],
Purpose extends "swagger" | "ajv" = "swagger",
Prefix extends string = Purpose extends "swagger"
? "#/components/schemas"
: "components#/schemas",
>(): IJsonApplication;
// SAFE PARSER FUNCTIONS
export function isParse<T>(input: string): T | null;
export function assertParse<T>(input: string): T;
export function validateParse<T>(input: string): IValidation<T>;
// FASTER STRINGIFY FUNCTIONS
export function stringify<T>(input: T): string; // unsafe
export function isStringify<T>(input: T): string | null; // safe
export function assertStringify<T>(input: T): string;
export function validateStringify<T>(input: T): IValidation<string>;
// FACTORY FUNCTIONS
export function createAssertParse<T>(): (input: string) => T;
export function createAssertStringify<T>(): (input: T) => string;
// +) createIsParse, createValidateParse
// +) createStringify, createIsStringify, createValidateStringifytypia supports enhanced JSON functions.
application(): generate JSON schema with only one line- you can complement JSON schema contents through comment tags
assertParse(): parse JSON string safely with type validationisStringify(): maximum 10x faster JSON stringify fuction even type safe
Measured on AMD R7 6800HS
Miscellaneous
export function random<T>(): Primitive<T>; // random data generator
export function clone<T>(input: T): Primitive<T>; // deep copy
export function prune<T>(input: T): void; // remove superfluous propertiesWhen you need test data, just generate it through typia.random<T>().
If a little bit special data being required, use (Features > Runtime Validators > Comment Tags)
Appendix
Nestia
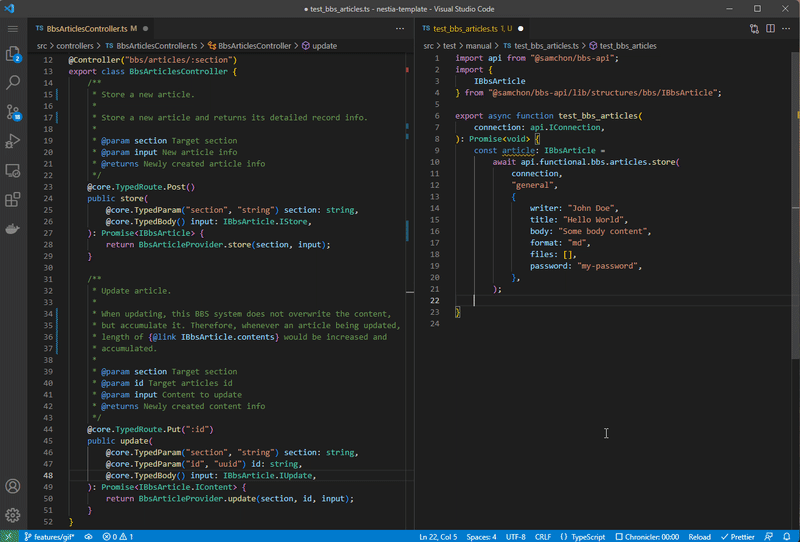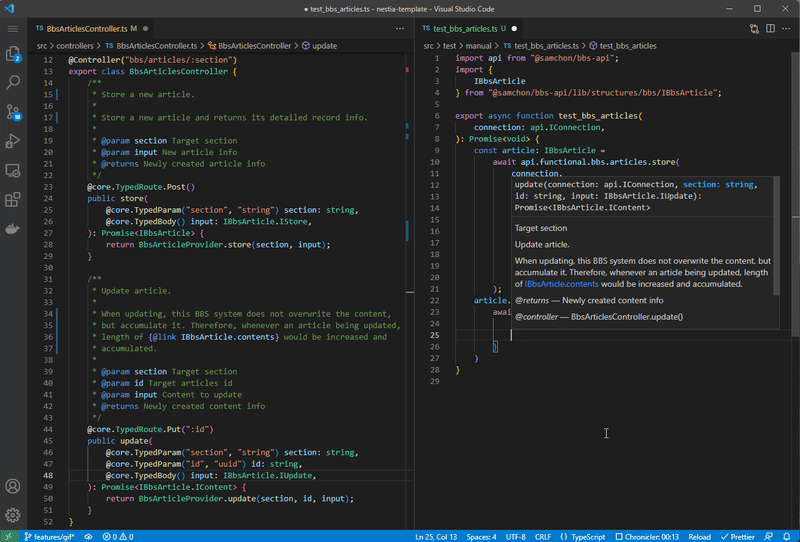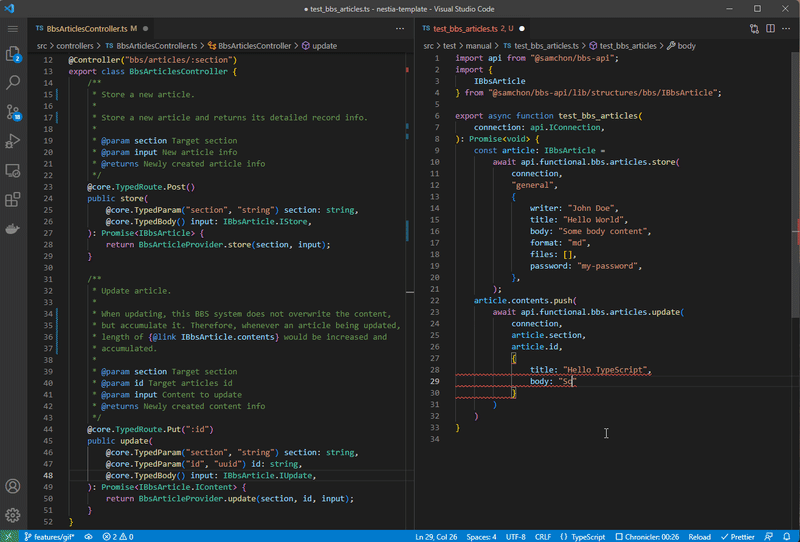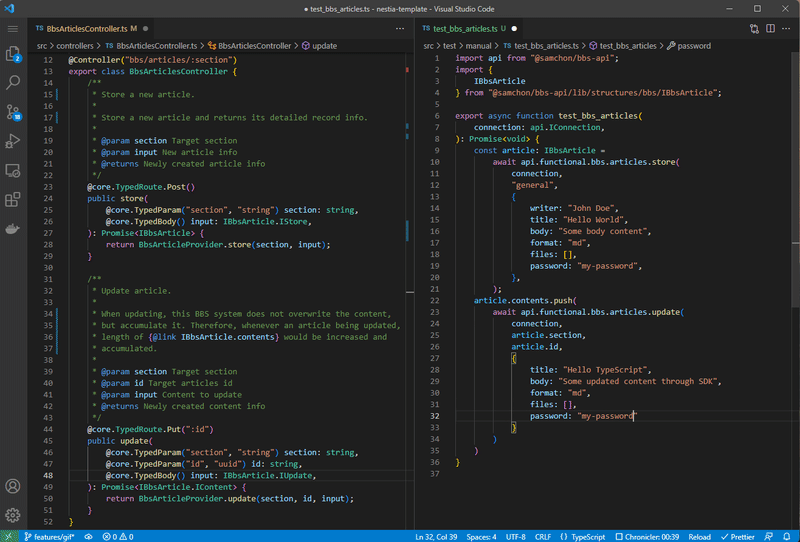
Nestia is a set of helper libraries for NestJS, supporting below features:
@nestia/core: 15,000x times faster validation decorators@nestia/sdk: evolved SDK and Swagger generators- SDK (Software Development Kit)
- interaction library for client developers
- almost same with tRPC
- SDK (Software Development Kit)
nestia: just CLI (command line interface) tool
Reactia
Not published yet, but soon
Reactia is an automatic React components generator, just by analyzing TypeScript type.
@reactia/core: Core Library analyzing TypeScript type@reactia/mui: Material UI Theme forcoreandnest@reactia/nest: Automatic Frontend Application Builder forNestJS

When you want to automate an individual component, just use @reactia/core.
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import typia from "typia";
import { ReactiaComponent } from "@reactia/core";
import { MuiInputTheme } from "@reactia/mui";
const RequestInput = ReactiaComponent<IRequestDto>(MuiInputTheme());
const input: IRequestDto = { ... };
ReactDOM.render(
<RequestInput input={input} />,
document.body
);Otherwise, you can fully automate frontend application development through @reactia/nest.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { ISwagger } "@nestia/swagger";
import { MuiApplicationTheme } from "@reactia/mui";
import { ReactiaApplication } from "@reactia/nest";
const swagger: ISwagger = await import("./swagger.json");
const App: React.FC = ReactiaApplication(MuiApplicationTheme())(swagger);
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.body
);



%20Core(TM)%20i5-1135G7%20%40%202.40GHz/images/is.svg)


