Package Exports
- @datastructures-js/set
This package does not declare an exports field, so the exports above have been automatically detected and optimized by JSPM instead. If any package subpath is missing, it is recommended to post an issue to the original package (@datastructures-js/set) to support the "exports" field. If that is not possible, create a JSPM override to customize the exports field for this package.
Readme
@datastructures-js/set
extends javascript ES6 Set class and implements new functions in it.
Table of Contents
Install
npm install --save @datastructures-js/setAPI
require
const EnhancedSet = require('@datastructures-js/set');import
import EnhancedSet from '@datastructures-js/set';javascript Set class
It extends ES6 Set class so it already has all the Set functionality.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Set
Construction
constructor accepts an optional array of elements same like Set.
Example
const set1 = new EnhancedSet(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D']);
const set2 = new EnhancedSet(['C', 'D', 'E', 'F']);.union(set)
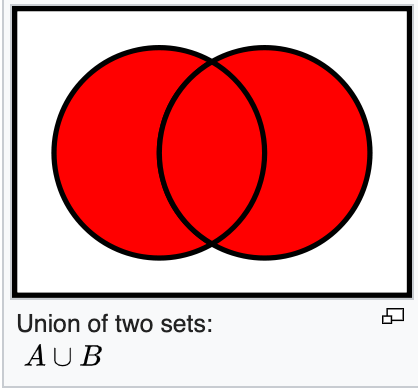
applies union with another set and returns a set with all elements of the two.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Union_(set_theory)
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n+m) |
n = number of elements of the first set m = number of elements of the second set |
| return |
|---|
| EnhancedSet |
Example
console.log(set1.union(set2)); // EnhancedSet { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' }.intersect(set)
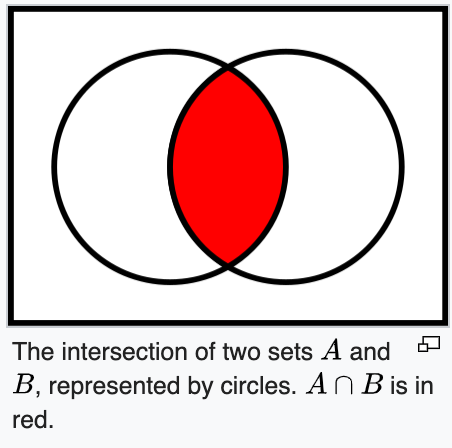
intersects the set with another set and returns a set with existing elements in both sets.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intersection_(set_theory)
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n) | n = number of elements of the set |
| return |
|---|
| EnhancedSet |
Example
console.log(set1.intersect(set2)); // EnhancedSet { 'C', 'D' }.complement(set)
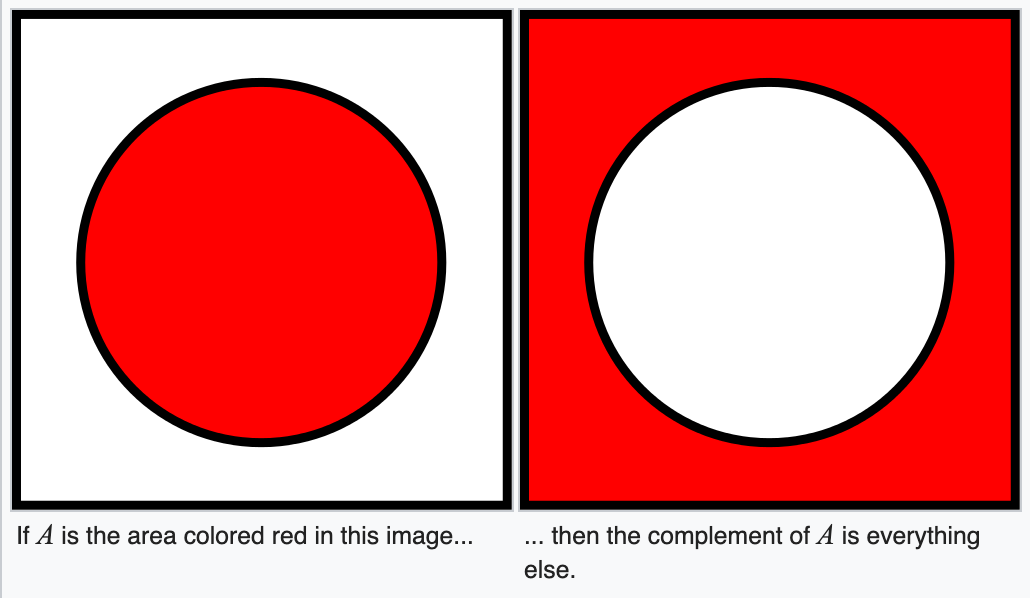
returns elements in a set and not in the other set relative to their union.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complement_(set_theory)
| return |
|---|
| EnhancedSet |
Example
console.log(set1.complement(set2)); // EnhancedSet { 'A', 'B' }
console.log(set2.complement(set1)); // EnhancedSet { 'E', 'F' }.isSubsetOf(set)
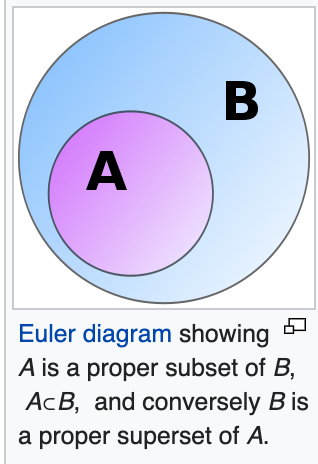
checks if the set is a subset of another set and returns true if all elements of the set exist in the other set.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subset
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n) | n = number of elements of the set |
| return |
|---|
| boolean |
Example
console.log(set1.isSubsetOf(new Set(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']))); // true
console.log(set1.isSubsetOf(set2)); // false.isSupersetOf(set)
checks if the set is a superset of another set and returns true if all elements of the other set exist in the set.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subset

| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n) | n = number of elements of the set |
Example
console.log(set1.isSupersetOf(new Set(['A', 'B']))); // true
console.log(set1.isSupersetOf(set2)); // false.product(set, separator)
applies cartesian product between two sets. Default separator is ,.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cartesian_product
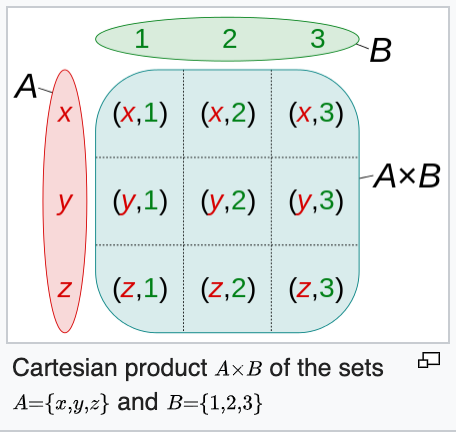
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| separator | string |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n*m) |
n = number of elements of the first set m = number of elements of the second set |
Example
console.log(set1.product(set2));
/*
EnhancedSet {
'A,C',
'A,D',
'A,E',
'A,F',
'B,C',
'B,D',
'B,E',
'B,F',
'C,C',
'C,D',
'C,E',
'C,F',
'D,C',
'D,D',
'D,E',
'D,F'
}
*/
console.log(set1.product(set2, ''));
/*
EnhancedSet {
'AC',
'AD',
'AE',
'AF',
'BC',
'BD',
'BE',
'BF',
'CC',
'CD',
'CE',
'CF',
'DC',
'DD',
'DE',
'DF'
}
*/.equals(set)
checks if two sets are equal.
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| set | Set |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n) | n = number of elements of the set |
| return |
|---|
| boolean |
Example
console.log(set1.equals(new Set(['B', 'A', 'D', 'C']))); // true
console.log(set1.equals(new EnhancedSet(['D', 'C']))); // false.filter(cb)
filters the set based on a callback and returns the filtered set.
| params | |
|---|---|
| name | type |
| cb | function |
| runtime | explanation |
|---|---|
| O(n) | n = number of elements of the set |
| return |
|---|
| EnhancedSet |
Example
console.log(set1.filter((el) => el > 'B')); // EnhancedSet { 'C', 'D' }.toArray()
converts the set into an array.
| return |
|---|
| array |
Example
console.log(set1.toArray()); // [ 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D' ]Build
grunt buildLicense
The MIT License. Full License is here


